 PDF(2941 KB)
PDF(2941 KB)


The influence of plant root splitting on garden rockeries in Jiangnan: taking the Zhanyuan Garden as an example
ZHANG Qingping, CHEN Fengyi
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 271-278.
 PDF(2941 KB)
PDF(2941 KB)
 PDF(2941 KB)
PDF(2941 KB)
The influence of plant root splitting on garden rockeries in Jiangnan: taking the Zhanyuan Garden as an example
【Objective】Jiangnan garden rockeries are a critical aspect of garden heritage. The widespread issue of plant root splitting poses a serious threat to the longevity and preservation of these rockeries. Incorporating the study of plant root splitting into the preventive protection system for rockeries can strengthen the system’s foundation, leading to a more effective preservation of garden heritage.【Method】This study uses the Zhanyuan Garden in Nanjing as a case study to quantitatively analyze the mechanism of plant root splitting in rockeries. It identifies problematic tree species, proposes and verifies five plant variables significantly related to root splitting, and establishes a regression prediction model for the area of cracks caused by this phenomenon.【Result】The study found that tree species with straight and deep roots are more likely to cause cracks in artificial rockeries. In the Zhanyuan Garden, the most significant root splitting was observed in Puja and privet, followed by loquat, Longjaya sophora, Magnolia, and papaya. Five factors,namely root length, root diameter, canopy width, tree height, and base diameter,were identified as highly influential in root splitting, showing significant correlations with the area of the resulting cracks. A multiple regression analysis helped to construct a preliminary prediction model for rockery crack areas, setting a warning threshold for changes in rockery crack dimensions. It was suggested that inhibiting the growth of a single root system might be necessary if the root length changes by more than 11.25 cm while the diameter remains constant.【Conclusion】Plant root splitting accelerates the development and expansion of cracks on rockery surfaces, potentially leading to stone fractures and structural collapse, thus endangering the heritage’s long-term preservation. Based on the quantitative analysis, refining environmental variables, categorizing monitoring levels, and defining clear warning indicators can enhance the predictive capabilities and quantitative assessments for rockery protection. These measures aim to facilitate timely interventions to mitigate the impact of root splitting and improve the overall preventive protection system for rockery heritage.
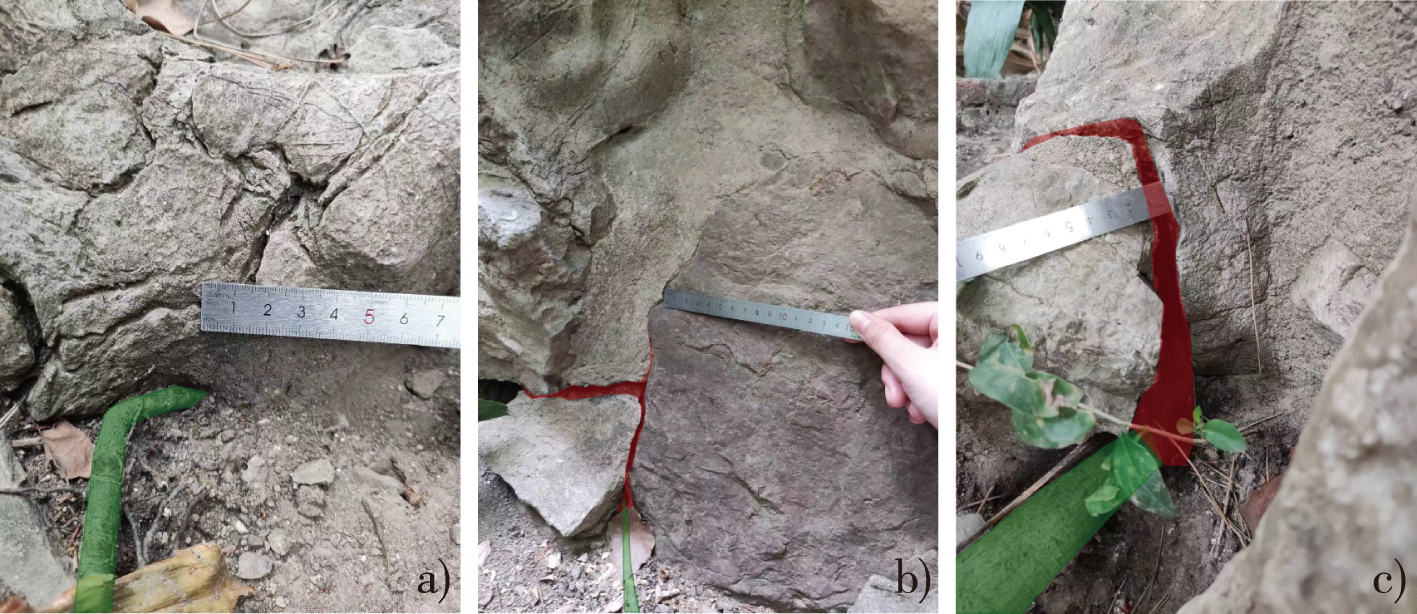
Jiangnan gardens / garden rockeries / root splitting action / rock mass cracks / preventive protection / Nanjing Zhanyuan Garden
| [1] |
端木山. 江南私家园林假山研究:起源与形态[D]. 北京: 中央美术学院, 2011.
|
| [2] |
徐亮, 李金宇. 石涛叠山作品的“人间孤本” 扬州片石山房:兼与曹汛先生商石涛寓扬期间造园史实[J]. 中国园林, 2014, 30(8):116-119.
|
| [3] |
朱子墨. 江南私家园林假山路径量化研究:以瞻园北假山、艺圃主假山、怡园主假山为例[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2020.
|
| [4] |
(明)计成. 园冶注释[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2020:37-45.
|
| [5] |
张莉. 苏州遗产园林植物造景现状与保护修复研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2020.
|
| [6] |
樊维. 裂隙岩体植物根劈作用机理研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2016.
|
| [7] |
张青萍, 董芊里, 傅力. 江南园林假山遗产预防性保护研究[J]. 建筑遗产, 2021(4):53-61.
|
| [8] |
梅雯. 园林遗产监测预警体系研究:以苏州古典园林为例[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2019.
|
| [9] |
程洪福, 胡伏原. 环秀山庄假山遗产监测探究[J]. 中国园林, 2021, 37(2):139-144.
|
| [10] |
刘甜, 赵晓文, 刘建军, 等. 对大型土遗址的植物病害研究:以西安阿房宫遗址为例[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 2019, 31(1):105-110.
|
| [11] |
赵晓文. 植物对土遗址裂隙的影响及其作用机理研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2014.
|
| [12] |
赵晓进, 梁芝栋, 邵立杰, 等. SPSS软件非线性回归功能的分析与评价[J]. 统计与决策, 2021, 37(23):20-22.
|
| [13] |
王姝, 柴建设. 基于社会科学统计程序(SPSS)回归性分析的尾矿库事故预测模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2008, 18(12):34-40,177.
|
| [14] |
查剑锐. 山东长清灵岩寺石质文物风化过程及保护材料研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2021.
|
| [15] |
凌建明, 孙钧. 脆性岩石的细观裂纹损伤及其时效特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 1993, 12(4):304-312.
|
| [16] |
赵毅鑫, 刘斌, 杨志良, 等. 神东矿区不同赋存深度沉积岩抗拉强度与断裂韧度研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(6):1732-1741.
|
| [17] |
凌建明, 孙钧. 应变空间表述的岩体损伤本构关系[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 1994, 22(2):135-140.
|
| [18] |
兰恒星, 吕洪涛, 包含, 等. 石窟寺岩体劣化机制与失稳机理研究进展[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 48(4):1603-1633.
|
| [19] |
汪东云, 付林森, 姚金石, 等. 北山石窟岩体风化现状及控制因素[J]. 重庆建筑工程学院学报, 1993, 15(1):81-86.
|
| [20] |
杨鸿锐, 刘平, 孙博, 等. 冻融循环对麦积山石窟砂砾岩微观结构损伤机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(3):545-555.
|
| [21] |
王翀, 王明鹏, 白崇斌, 等. 陕西省露天石质文物藻类、地衣、苔藓调查[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 2015, 27(4):76-82.
|
| [22] |
张永, 武发思, 苏敏, 等. 石质文物的生物风化及其防治研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(11):3980-3990.
|
| [23] |
张兵峰. 川渝石窟裂隙水病害机理研究:以大足石刻大佛湾卧佛区域为例[J]. 中国文化遗产, 2018(4):27-34.
|
| [24] |
徐方圆, 吴来明, 解玉林, 等. 文物保存环境中温湿度评估方法研究[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 2012, 24(S1):6-12.
|
| [25] |
周安庆. “金陵第一名园” 的神姿风采:清代袁江及其《瞻园图》画卷释读[J]. 收藏界, 2014(2):66-69.
|
| [26] |
强大双. 江南古典私家园林旅游环境容量测算及调控研究:以南京瞻园为例[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2016.
|
| [27] |
周格至. 南京古典私家园林历史考证与特征研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2019.
|
| [28] |
张青萍, 毛清, 贾星星. 瞻园假山的植物景观空间尺度变迁研究[J]. 中国园林, 2022, 38(2):42-47.
|
| [29] |
李斌, 谢东辉, 丁勇, 等. 基于图像处理和标识物的裂缝变化测量方法[J]. 工程质量, 2022, 40(8):69-74.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
吴美萍. 预防性保护理念下建筑遗产监测问题的探讨[J]. 华中建筑, 2011, 29(3):169-171.
|
| [32] |
刘彦婷. 岩体裂缝动态识别算法研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2012.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |