 PDF(1940 KB)
PDF(1940 KB)


Construction and application of the leaf area prediction model for young Quercus variabilis
LI Hui, ZHANG Wan, CHANG Yihao, YANG Xia, XIAO Xiangwei, ZHU Jingle
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 246-254.
 PDF(1940 KB)
PDF(1940 KB)
 PDF(1940 KB)
PDF(1940 KB)
Construction and application of the leaf area prediction model for young Quercus variabilis
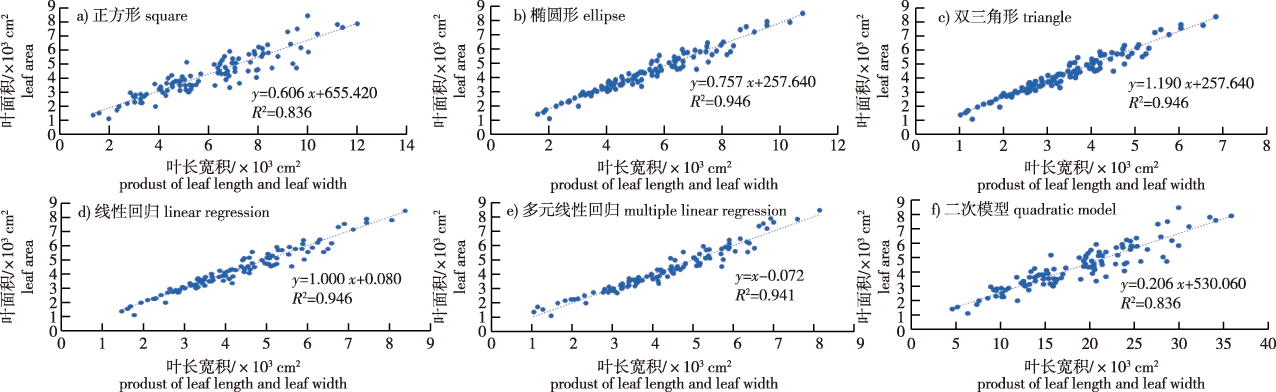
【Objective】The leaf area prediction model of young Quercus variabilis was established to apply a rapid and nondestructive measurement. The leaf shape variation and difference characteristics of 43 different Q. variabilis families were analyzed to provide a theoretical basis for studying the genetic diversity and breeding of Q. variabilis. 【Method】A total of 43 Q. variabilis families were selected from different regions of China as the research objects. The optimal parameters of the leaf area prediction model were selected through correlation analysis and curve fitting analysis of leaf length, width, length-width ratio, length-width product, and measured leaf area.Through geometric model and curve fitting analysis, the optimal prediction model of the leaf area of young Q. variabilis was screened, and the results were verified. The differences in leaves among different families were analyzed by statistical description, one-way analysis of variance, correlation analysis, and cluster analysis. 【Result】(1) Leaf length-width product (X1×X2) was significantly correlated with the leaf area of young Q. variabilis, and the prediction model of leaf area of young Q. variabilis could be established according to this combination index. (2) The leaf area prediction model of young Q. variabilis Y=0.595X1 ×X2+257.640 was the most accurate, R2=0.946, and the standard error was as low as 32.830 cm2, which could be used to predict the leaf area of young Q. variabilis.(3) The leaf indexes of the 43 Q. variabilis families had different degrees of variation. The differences in leaves among different families and within families were large. (4) The results of the correlation analysis between leaf traits and geographical information of origin showed no significant correlation between other indexes except leaf dry weight and annual precipitation. 43 families could not be classified independently, and the regularity was not strong. 【Conclusion】A more accurate prediction model of the leaf area of young Q. variabilis Y=0.595X1×X2+257.640 was established by using leaf length and width product as parameters, which provided an efficient and nondestructive method for obtaining the leaf area of Q. variabilis and provided a theoretical basis for breeding and family selection of Q. variabilis.
Quercus variabilis family / leaf area prediction model / leaf shape / variation characteristics
| [1] |
李娟霞, 田青. 兰州市6种园林植物叶片形态和光合生理特征[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(1):72-80.
|
| [2] |
魏龙鑫, 章异平, 李艺杰, 等. 栓皮栎叶片和枝条非结构性碳水化合物调配关系研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(2):96-102.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
薛雪, 张金池, 孙永涛, 等. 上海常绿树种固碳释氧和降温增湿效益研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 40(3):81-86.
|
| [7] |
孙文勇, 肖小华, 王玉芳, 等. 十堰市引种栽培油橄榄品种的叶片与果实表型性状分析[J]. 湖北林业科技, 2022, 51(3):10-13.
|
| [8] |
罗芊芊, 周志春, 邓宗付, 等. 南方红豆杉天然居群叶片的表型性状和氮磷化学计量特征的变异规律[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2021, 30(1):27-35.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
于秋香, 刘警, 李扬, 等. 核桃种质资源叶片表型性状的遗传多样性研究[J]. 农业科学与技术:英文版, 2021, 22(1):1-8.
|
| [11] |
仲磊, 张焕朝, 范俊俊, 等. 夏季淹水胁迫对北美枫香苗木叶色及光合荧光特性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(2):69-76.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
吴凤婵, 李安定, 蔡国俊, 等. 6种西番莲属(Passiflora)植物叶面积经验模型构建[J]. 果树学报, 2021, 38(9):1600-1610.
|
| [15] |
彭曦, 闫文德, 王光军, 等. 杉木叶形态特征与叶面积估算模型[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(10):3569-3580.
|
| [16] |
杜尚嘉, 王鑫, 吴海霞, 等. 海南风吹楠成熟叶叶面积估算模型建立[J]. 热带林业, 2021, 49(4):17-21.
|
| [17] |
巫娟, 胡姝珍, 茅思雨, 等. 基于叶片形态的毛竹单叶叶面积模型[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(8):47-54.
|
| [18] |
王进杰, 杨军, 胡姝珍, 等. 3种丛生竹叶面积预测模型研究[J]. 南方林业科学, 2020, 48(1):7-12.
|
| [19] |
谈丽华, 巫娟, 胡妹珍, 等. 基于叶形分类的淡竹叶面积预测模型研究[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2020, 18(1):6-10.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
张鹏, 杨颖, 奚如春, 等. 高州油茶种群叶片性状变异分析[J]. 林业与环境科学, 2018, 34(5):13-19.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
杨红云, 路艳, 孙爱珍, 等. 水稻叶片几何参数无损测量方法研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2020, 42(2):407-418.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
李理渊, 李俊, 同小娟, 等. 不同光环境下栓皮栎和刺槐叶片光合光响应模拟[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(7):2295-2306.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |