 PDF(1817 KB)
PDF(1817 KB)


Plant hormones and metabolites response to feeding stimulation by pine caterpillar (Dendrolimus tabulaeformis) and leaf clipping control in Chinese pine (Pinus tabuliformis)
ZHAO Ya’nan, SUN Tianhua, WANG Lifeng, XU Qiang, LIU Junxia, GAO Baojia, ZHOU Guona
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 219-226.
 PDF(1817 KB)
PDF(1817 KB)
 PDF(1817 KB)
PDF(1817 KB)
Plant hormones and metabolites response to feeding stimulation by pine caterpillar (Dendrolimus tabulaeformis) and leaf clipping control in Chinese pine (Pinus tabuliformis)
【Objective】This experiment was conducted with the aim of defining changes in metabolic pathways in response to mandibulate insect feeding and providing references for the growth and protection of Chinese pine (Pinus tabuliformis).【Method】Pure P. tabuliformis forest in good growth status in Huangtuliangzi Forest Farm of Pingquan City, Chengde City, Hebei Province was the experimental field. Branches with consistent branch length and height above the ground in four directions were stimulated by ten pine caterpillars (Dendrolimus tabulaeformis) for feeding stimulation and leaf clipping control for mechanical damage. The pine needles were collected 3 cm below the chewing or cutting sites. The CK group received no treatment (0 h, recorded as 0 h), and 10 intact pine needles were collected. Metabolome and total flavonoid contents were measured in the needles at 0, 2 and 8 h after the different treatment modes. The plant hormones JA, SA, IAA and ABA were measured using needles at 0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 4.0, 6.0, and 8.0 h after different treatments.【Result】Analysis of metabolomics showed that the top three pathways mainly annotated and enriched for DAMs compared to 2.0 h after FS and LCC are flavonoid biosynthesis, amino acid metabolism, and arginine and proline metabolism; the top three pathways mainly annotated and enriched for DAMs compared to 8.0 h after FS and LCC are flavonoid biosynthesis, linoleic acid metabolism, and flavonoid and flavonol biosynthesis. Thus, D. tabulaeformis feeding stimulation can significantly induce the upregulation of flavonoid expression at the chewing sites of needles when compared to the leaf clipping control. The plant hormones, JA and IAA, showed expression trends consistent with those of the corresponding substances in the metabolome. A significant positive correlation between JA and SA, JA and IAA and IAA and ABA (P< 0.05) was observed. 【Conclusion】Thus, the flavonoid pathway is one of the main pathways involved in resistant formation in conifers. Simple damage mechanisms did not induce significant differences in JA, IAA and ABA; thus, JA, IAA and ABA are involved in the development of resistance and growth during biotic stress.
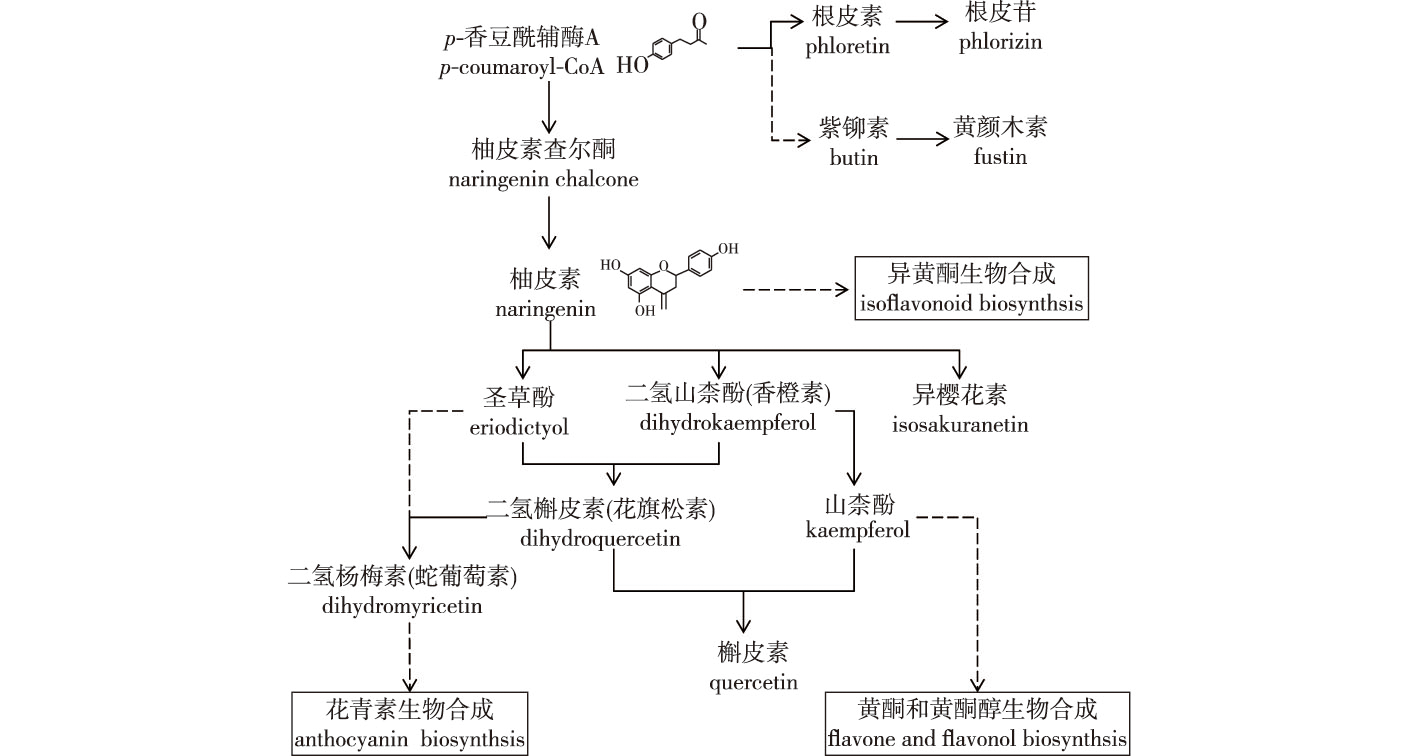
Pinus tabuliformis / Dendrolimus tabulaeformis / feeding stimulation / induced resistant / plant hormone / flavonoid pathway / metabolome
| [1] |
窦宏双, 梁晓, 陈青, 等. 二斑叶螨为害前后抗、感木薯转录组分析及水杨酸、茉莉酸途径差异表达基因验证[J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(11): 3146-3155.
|
| [2] |
黄双杰, 曹梦珍, 陈凌芝, 等. 氮素胁迫条件下茶树根系发育及生长素的响应[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2023, 39(3):814-821.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
赵利, 钞建宾, 郭捷, 等. 基于代谢组学技术的植物抗病相关代谢物研究进展[J]. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(6):1071-1078.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
张佳松. 甘蔗响应黏虫取食的代谢组学分析[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2020.
|
| [8] |
张强, 周鹏, 刘昌来, 等. NaCl处理下全缘冬青和红果冬青根系的转录组活性比较[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(3): 99-108.
|
| [9] |
张斌, 高宝嘉, 刘洋. 剪叶和取食刺激对油松体内几种防御酶的活性及其动态的影响[J]. 生态科学, 2017, 36(1):118-122.
|
| [10] |
石媛媛, 冯金周, 于连海, 等. 昆虫取食和剪叶刺激对油松针叶内部分防御物质的诱导效应[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2017, 40(1):81-86.
|
| [11] |
王银翠, 周国娜, 张斌, 等. 油松毛虫取食和剪叶刺激胁迫下油松的蛋白质表达差异分析[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(8):68-75.
|
| [12] |
秦世杰, 祁金玉, 刘仁军, 等. 自然状态下油松感染松材线虫后的生理响应[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2021, 52(5):625-632.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
徐展宏, 朱莹, 金慧颖, 等. 不同叶色青钱柳叶片色素、多酚含量及光合特性的差异[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(2):103-110.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
王伟伟. 茶树对茶尺蠖的抗性评价及其抗性机制研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
李永华, 肖能文, 刘勇波. 植物防御中茉莉酸信号通路抑制与终止的作用机制[J]. 植物保护学报, 2021, 48(3):563-569.
|
| [25] |
邓苗苗, 郭晓黎. 植物响应寄生线虫侵染机制的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37(7):25-34.
|
| [26] |
叶德友, 漆永红, 李敏权. 植物与线虫互作的信号传导及调控机制研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(10):191-201.
|
| [27] |
张瑾, 邢玉娴, 韩涛, 等. 茶树诱导抗虫性的研究进展[J]. 昆虫学报, 2022, 65(3):399-408.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
丁旭, 黄茜, 邓沁宇, 等. 脱落酸在植物抗虫性中的作用研究进展[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2019, 41(4):808-813.
|
| [31] |
张吉玲, 李明阳, 李勇, 等. 机械损伤处理杉木无性系萌蘖及内源激素含量差异[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(2): 153-158.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
岳喜良, 秦健, 洑香香, 等. 氮素水平对青钱柳叶片主要次生代谢物含量和抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(2): 35-42.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |