 PDF(2522 KB)
PDF(2522 KB)


Analysis of genetic diversity and construction of core collections of Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) natural population
YAN Pingyu, ZHANG Lei, WANG Jiaxing, FENG Kele, WANG Haohao, ZHANG Hanguo
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 69-80.
 PDF(2522 KB)
PDF(2522 KB)
 PDF(2522 KB)
PDF(2522 KB)
Analysis of genetic diversity and construction of core collections of Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) natural population
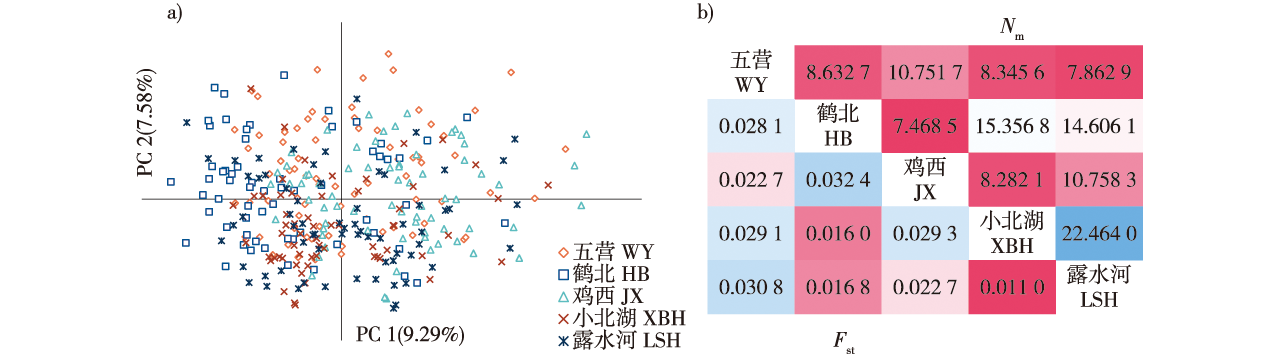
【Objective】 Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) is a valuable tree species that is distributed throughout northeastern China. Over the past century, human interference has led to a gradual decrease in the number of individuals and distribution of its natural population. Assessing the genetic diversity and building a core collection of natural Korean pine could provide a scientific basis for the effective conservation, management, and utilization of Korean pine germplasm resources. 【Method】 A total of five well-preserved natural populations of Korean pine in Hebei, Wuying, Xiaobeihu and Jixi in Heilongjiang Province and Lushuihe in Jilin Province in northeast China were studied. A combination of phenotypic data and molecular markers was used to construct the core collection. 【Result】 Molecular and phenotypic ANOVA results showed that the genetic variation of Korean pine natural populations mainly originated from inter-individual differences, which accounted for 96% and 72.84% of the total variation, respectively. The Jixi population was genetically distant from other populations, with an average Fst of 0.026 8. It also had a high genetic diversity, with Shannon and phenotypic diversity index values of 1.111 and 2.00, respectively. The population structure analysis showed that the five Korean pine natural populations had no obvious subpopulation structure. There were no significant changes in the genetic diversity of Korean pine populations among the different forest ages. Additionally, in the younger forest there was no evidence of heterozygous deletions or inbreeding. There was a broad correlation between needle traits and geographic factors, resulting in the phenotypic differentiation of Korean pine populations. 【Conclusion】 The Shannon and phenotypic diversity indexes of the core collection constructed by combining molecular and phenotypic markers with a 30% sampling ratio were 1.076 and 2.018, respectively, which was representative of the genetic status of Korean pine populations. This information can be used to better manage the germplasm resources of Korean pine and promote its protection and use. The genetic structure characteristics indicated a need to focus on in situ protection of the natural germplasm and to promote ecological recovery, germplasm protection, and use of Korean pine.
Korean pine(Pinus koreciensis) / natural populations / genetic diversity / genetic structure / core collection / forest breeding / native trees
| [1] |
马建路, 庄丽文, 陈动, 等. 红松的地理分布[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 1992, 20(5):40-48.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
张振, 张含国, 莫迟, 等. 红松转录组SSR分析及EST-SSR标记开发[J]. 林业科学, 2015, 51(8):114-120.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
王欢利, 严灵君, 黄犀, 等. 南京椴群体遗传多样性和遗传结构分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(1):145-153.
|
| [6] |
顾万春. 森林遗传资源学概论[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 1998.
|
| [7] |
尚占环, 姚爱兴. 生物遗传多样性研究方法及其保护措施[J]. 宁夏农学院学报, 2002, 23(1):66-69.
|
| [8] |
张巍, 王清君, 郭兴. 红松不同种源的遗传多样性分析[J]. 森林工程, 2017, 33(2):17-21.
|
| [9] |
童茜坪, 剡丽梅, 张磊, 等. 红松种子园单株ISSR-PCR遗传多样性分析[J]. 林业科技, 2020, 45(2):17-20.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
李自超, 张洪亮, 曾亚文, 等. 云南地方稻种资源核心种质取样方案研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2000, 33(5):1-7.
|
| [13] |
赵冰, 张启翔. 中国蜡梅种质资源核心种质的初步构建[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2007, 29(S1):16-21.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
夏德安, 杨书文, 杨传平, 等. 红松种源试验研究(Ⅰ):种源的初步区划[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 1991, 19(S2):122-128.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
倪州献, 白天道, 蔡恒, 等. 马尾松基因组SSR标记在松属其他树种中的通用性分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2015, 13(12):2811-2817.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
何启平, 陈莹. 校园常见植物叶绿素提取方法比较及其含量测定[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2015, 38(10):117-120.
|
| [31] |
樊文强, 盖红梅, 孙鑫, 等. SSR数据格式转换软件DataFormater[J]. 分子植物育种, 2016, 14(1):265-270.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
徐存宝, 刘滨凡, 刘维斌. 天然红松林结构规律的探讨[J]. 林业科技, 1991, 16(4):17-19.
|
| [37] |
郭文丽, 李义良, 赵奋成, 等. 湿加松无性系表型遗传多样性研究[J]. 植物研究, 2019, 39(2):259-266.
|
| [38] |
陈存, 丁昌俊, 黄秦军, 等. 美洲黑杨表型核心种质库构建[J]. 林业科学研究, 2021, 34(2):1-11.
|
| [39] |
贾丙瑞, 周广胜, 刘永志, 等. 中国天然林凋落物量的空间分布及其影响因子分析[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2016, 46(11):1304-1311.
|
| [40] |
徐海明. 种质资源核心库构建方法的研究及其应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2005.
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
冯富娟, 隋心, 张冬东. 不同种源红松遗传多样性的研究[J]. 林业科技, 2008, 33(1):1-4.
|
| [43] |
张亚红, 贾会霞, 王志彬, 等. 滇杨种群遗传多样性与遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4):355-365.
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
邵丹, 裴赢, 张恒庆. 凉水国家自然保护区天然红松种群遗传多样性在时间尺度上变化的cpSSR分析[J]. 植物研究, 2007, 27(4):473-477.
|
| [46] |
李斌, 顾万春, 卢宝明. 白皮松天然群体种实性状表型多样性研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2002, 10(2):181-188.
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
陈向向, 盖中帅, 翟军团, 等. 中国西北地区天然胡杨群体遗传多样性及核心保护单元的构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12):1638-1649.
|
| [51] |
陈存, 丁昌俊, 张静, 等. 美洲黑杨群体结构分析及核心种质库构建[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(9):67-76.
|
| [52] |
徐益, 张列梅, 郭艳春, 等. 黄麻核心种质的遴选[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(11):1672-1681.
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
武星彤, 陈璐, 王敏求, 等. 丹霞梧桐群体遗传结构及其遗传分化[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11):1168-1179.
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
吕锋, 解孝满, 韩彪, 等. 基于SSR标记的麻栎天然群体遗传多样性分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(3):109-116.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |