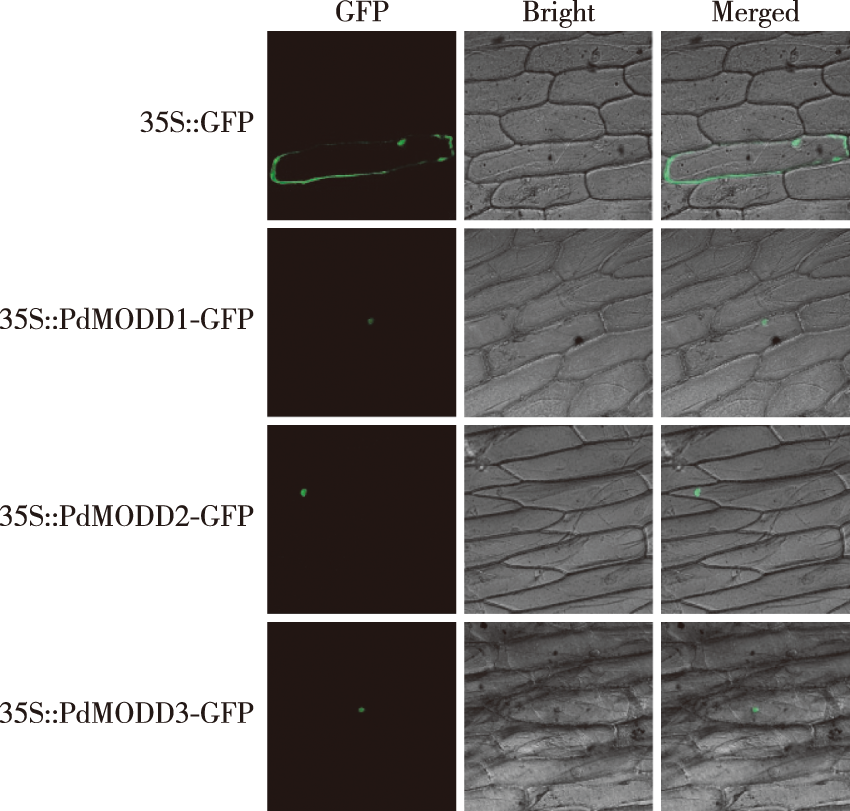
【Objective】To explore the function of PdMODD in the growth and development of Populus × euramericana, we analyzed their sequence characteristics, subcellular localization and expression patterns in response to salt and drought stress, which will provide a theoretical basis for revealing the molecular mechanisms of stress resistance and breeding new poplar varieties. 【Method】Based on the rice MODD amino acid sequence, Podel.08G114100, Podel.10G158900 and Podel.17G098500 were selected using BLAST in the genome of Populus deltoides WV94 v2.1. Using these gene sequences as references and Populus × euramericana ‘Bofeng 3 hao’ cDNA as template, three genes (PdMODD1,PdMODD2 and PdMODD3) were cloned. The structural characteristics of the PdMODD protein and its genetic relationship with its homologous proteins were analyzed using bioinformatics methods. The subcellular localization of PdMODD genes was analyzed using particle bombardment. The expression characteristics of PdMODD genes in different tissues and their response to different stresses were analyzed using qRT-PCR. 【Results】The open reading frames of PDMODD1-PDMODD3 genes were 1 065, 1 065 and 1 074 bp, encoding 354, 354 and 357 amino acids, respectively, all of which were unstable hydrophilic proteins located in the nucleus.PdMODD genes are all members of the NINJA family and contain three conserved domains, one of which is the transcriptional repression motif EAR. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that PdMODD1 protein was closely related to PtAFP2 (Populus trichocarpa) and located in the same branch as AtAFP1 (Arabidopsis thaliana) and MeAFP2 (Manihot esculenta). PdMODD2 protein had a close relationship with JcAFP2 (Jatropha curcas) and converged into a branch with AtAFP2; PdMODD3 was closely related to PtAFP3-1 and located in the same branch as QsAFP3 (Quercus suber) and AtAFP4. The subcellular localization results showed that PdMODD genes were localized in the nucleus. The results of tissue specificity analysis showed that PdMODD genes were highly expressed in the leaves and the least expressed in the roots. The expression patterns of stress response showed that under NaCl and PEG stress, PdMODD1, PdMODD2 and PdMODD3 were significantly upregulated in the root, stem and leaf tissues. 【Conclusion】PdMODD1-PdMODD3 are all members of the NINJA family, with the conserved transcriptional repression motif EAR and tissue specificity. They were highly expressed in the leaves, significantly induced by NaCl and PEG stress, and were in a branch with AtAFP1, AtAFP2 and AtAFP4, which had negative regulatory effects on ABA and salt stress. It is hypothesized that PdMODD1, PdMODD2 and PdMODD3 may play an important regulatory role in response to P. euramericana ‘Bofeng 3 hao’ salt and drought stress.
 PDF(4500 KB)
PDF(4500 KB)


 PDF(4500 KB)
PDF(4500 KB)
 PDF(4500 KB)
PDF(4500 KB)