JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY ›› 2023, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (3): 173-181.doi: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202112035
Previous Articles Next Articles
XU Zihan1( ), WANG Lei2, CUI Ming1,*(
), WANG Lei2, CUI Ming1,*( ), LIU Yuguo1, ZHAO Ziqing1, LI Jiahao1
), LIU Yuguo1, ZHAO Ziqing1, LI Jiahao1
Received:2021-12-23
Revised:2022-01-24
Online:2023-05-30
Published:2023-05-25
Contact:
CUI Ming
E-mail:1375363747@qq.com;cuim@caf.ac.cn
CLC Number:
XU Zihan, WANG Lei, CUI Ming, LIU Yuguo, ZHAO Ziqing, LI Jiahao. Soil stoichiometry characteristics of different vegetation restoration modes in water source area of South-to-North Water Diversion Project[J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(3): 173-181.
Table 1
Basic situation of the study area"
| 样地类型 sample type | 平均海拔/m average altitude | 坡度/(°) slope | 胸径/cm DBH | 树高/m tree hight | 林分密度/ (株·hm-2) stand density | 土壤类型 soil type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 栓皮栎Quercus variabilis | 617 | 34 | 16.2±6.74 | 14.4±5.53 | 1 816 | 石灰土 |
| 侧柏Platycladus orientalis | 561 | 29 | 8.5±2.46 | 6.8±1.54 | 2 261 | 石灰土 |
| 杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata | 681 | 23 | 16.4±6.64 | 16.2±6.71 | 2 211 | 石灰土 |

Fig.1
Total soil nutrient mass fraction in different soil layers under different vegetation restoration modes Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different soil layers of the same stand (P <0.05). Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different stands in the same soil layer (P<0.05). The same below."
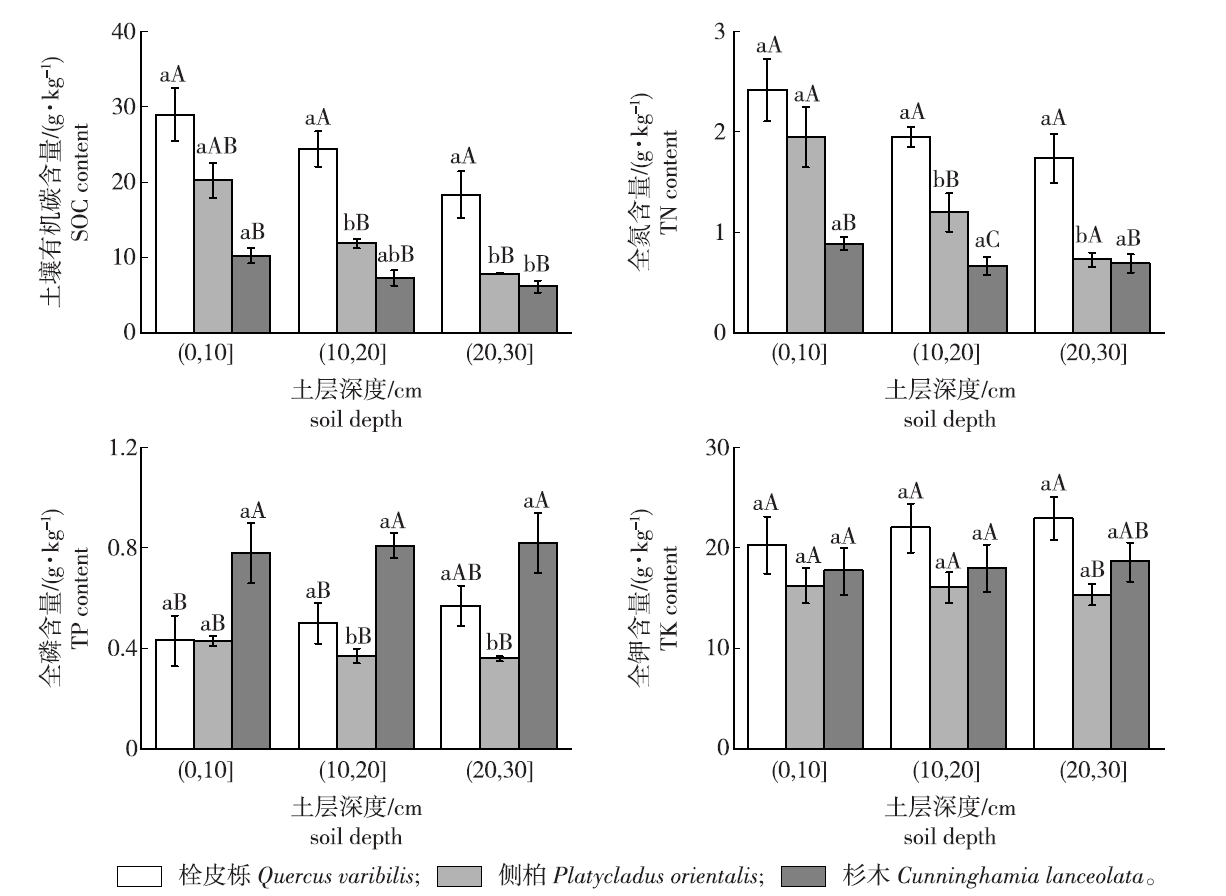
Table 2
The variation analysis of soil nutrients and stoichiometric characteristics in different vegetation restoration modes"
| 样地 plot | 统计项 statistic item | SOC/ (g·kg-1) | TN/ (g·kg-1) | TP/ (g·kg-1) | TK/ (g·kg-1) | C∶N | C∶P | C∶K | N∶P | N∶K | P∶K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 栓皮栎林 Q. varibilis | 平均值mean | 23.91 | 2.04 | 0.50 | 21.74 | 11.51 | 54.99 | 1.17 | 4.64 | 0.10 | 0.02 |
| 标准差SD | 4.36 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 1.08 | 0.95 | 19.29 | 0.30 | 1.45 | 0.02 | 0.00 | |
| 变异系数/% CV | 18.22 | 13.96 | 11.43 | 4.97 | 8.27 | 35.07 | 26.15 | 31.21 | 21.61 | 7.30 | |
| 侧柏林 P. orientalis | 平均值mean | 13.34 | 1.29 | 0.39 | 15.90 | 10.61 | 33.80 | 0.86 | 3.26 | 0.08 | 0.02 |
| 标准差SD | 5.16 | 0.50 | 0.03 | 0.38 | 3.11 | 29.79 | 38.05 | 30.76 | 37.92 | 7.22 | |
| 变异系数/% CV | 38.70 | 38.85 | 7.99 | 2.38 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.07 | |
| 杉木林 C. lanceolate | 平均值mean | 7.88 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 18.08 | 10.42 | 10.02 | 0.45 | 0.61 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| 标准差SD | 1.72 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.38 | 1.10 | 2.65 | 0.10 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.00 | |
| 变异系数/% CV | 21.76 | 13.24 | 2.12 | 2.09 | 10.53 | 26.42 | 23.00 | 49.67 | 13.68 | 3.44 |
Table 3
The correlation between soil nutrients and ecological stoichiometry characteristics"
| 指标index | SOC | TN | TP | TK | C∶N | C∶P | C∶K | N∶P | N∶K | P∶K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC | 1.000 | |||||||||
| TN | 0.977** | 1.000 | ||||||||
| TP | -0.458* | -0.453* | 1.000 | |||||||
| TK | 0.210 | 0.184 | 0.100 | 1.000 | ||||||
| C∶N | 0.456* | 0.280 | -0.296 | 0.153 | 1.000 | |||||
| C∶P | 0.922** | 0.889** | -0.633** | 0.071 | 0.432* | 1.000 | ||||
| C∶K | 0.910** | 0.902** | -0.482* | -0.178 | 0.363 | 0.901** | 1.000 | |||
| N∶P | 0.909** | 0.909** | -0.663** | 0.038 | 0.314 | 0.987** | 0.902 | 1.000 | ||
| N∶K | 0.854** | 0.894** | -0.475* | -0.242 | 0.175 | 0.843** | 0.974** | 0.879** | 1.000 | |
| P∶K | -0.508** | -0.495** | 0.873** | -0.361 | -0.326 | -0.605** | -0.370 | -0.620** | -0.337 | 1.000 |
| [1] | YU Y H, CHI Y K. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of soil at different depths in a Karst Plateau Mountain Area of China[J]. Pol J Environ Stud, 2019, 29(1): 969-978. DOI: 10.15244/pjoes/102781. |
| [2] | 贺金生, 韩兴国. 生态化学计量学:探索从个体到生态系统的统一化理论[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(1):2-6. |
| HE J S, HAN X G. Ecological stoichiometry: searching for unifying principles from individuals to ecosystems[J]. Chin J Plant Eco, 2010, 34(1):2-6. DOI: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2010.01.002. | |
| [3] | 刘立斌, 钟巧连, 倪健. 贵州高原型喀斯特次生林 C、N、P 生态化学计量特征与储量[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(22): 8606-8614. |
| LIU L B, ZHONG Q L, NI J. Ecosystem C∶N∶P stoichiometry and storages of a secondary plateau-surface Karst forest in Guizhou Province, southwestern China[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2019, 39(22): 8606-8614. DOI: 10.5846/stxb201805311207. | |
| [4] | 章广琦, 张萍, 陈云明, 等. 黄土丘陵区刺槐与油松人工林生态系统生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(4): 1328-1336. |
| ZHANG G Q, ZHANG P, CHEN Y M, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia and Pinus tabuliformis plantation ecosystems in the Loess hilly-gully region, China[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2018, 38(4): 1328-1336. DOI: 10.5846/stxb201701030010. | |
| [5] | 吴鹏, 崔迎春, 赵文君, 等. 喀斯特森林植被自然恢复过程中土壤化学计量特征[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(3): 80-92. |
| WU P, CUI Y C, ZHAO W J, et al. Characteristics of soil stoichiometric in natural restoration process of Maolan Karst forest vegetation, southwestern China[J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2019, 41(3): 80-92. DOI: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20180136. | |
| [6] | 王芳芳, 余凤荣, 童晨, 等. 河南省新安县郁山林区土壤速效养分分析[J]. 生态科学, 2021, 40(2): 67-73. |
| WANG F F, YU F R, TONG C, et al. Analysis of soil available nutrients in Yushan forest area of Xin’an County, Henan Province[J]. Ecol Sci, 2021, 40(2): 67-73. DOI: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2021.02.009. | |
| [7] | 王璐, 喻阳华, 邢容容, 等. 喀斯特高原山地区主要人工林土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 南方农业学报, 2017, 48(8): 1388-1394. |
| WANG L, YU Y H, XING R R, et al. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soils from main plantations in Karst Plateau mountainous area[J]. J South Agric, 2017, 48(8): 1388-1394. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2017.08.09. | |
| [8] | 王磊, 崔明, 周梦玲, 等. 河南省淅川县岩溶区不同恢复年限天然次生林植物群落特征[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(4): 720-728. |
| WANG L, CUI M, ZHOU M L, et al. Plant community characteristics of natural secondary forest with different restoration years in Karst area of Xichuan County, Henan Province[J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2020, 37(4): 720-728. DOI: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190498. | |
| [9] | 刘哲. 南水北调中线水源区淅川县石质荒漠化特征及防治技术研究[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2018. |
| LIU Z. Study on the characteristics and prevention and cure techniques of stony desertification in Xichuan County of the middle line of water diversion from the south to the north[D]. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2018. | |
| [10] | 顾汪明, 周金星, 武建宏, 等. 南水北调中线渠首淅川县石漠化治理现状与人工造林技术[J]. 林业资源管理, 2018(3): 44-48. |
| GU W M, ZHOU J X, WU J H, et al. Artificial afforestation technology for rocky desertification control in Xichuan County of south to north water diversion project[J]. For Resour Manag, 2018(3): 44-48. DOI: 10.13466/j.cnki.lyzygl.2018.03.009. | |
| [11] | 勇毫, 郭占胜, 杨朝兴, 等. 丹江口库区石漠化现状及治理措施研究:以河南省淅川县为例[J]. 河北农业科学, 2012, 16(2): 75-77. |
| YONG H, GUO Z S, YANG C X, et al. Study on status and control measures of rocky desertification in Danjiangkou Reservoir area: a case of Xichuan County,He’nan Province[J]. J Hebei Agric Sci, 2012, 16(2): 75-77. DOI: 10.16318/j.cnki.hbnykx2012.02.001. | |
| [12] | 张君, 蔡德宝, 杨树琼, 等. 丹江口库区不同坡度对土壤肥力特征的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(2): 32-38. |
| ZHANG J, CAI D B, YANG S Q, et al. Soil fertility characteristics of different slopes in the Danjiangkou Reservoir area[J]. Soils Fertil Sci China, 2021(2): 32-38. DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.20014. | |
| [13] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| BAO S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. | |
| [14] | CAO Y B, WANG B T, WEI T T, et al. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics and element reserves of three stands in a closed forest on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Environ Monit Assess, 2016, 188(2): 80. DOI: 10.1007/s10661-015-5057-6. |
| [15] | BATJES N H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world[J]. Eur J of Soil Sci, 1996, 47(2):151-163. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1996.tb01386.x. |
| [16] | BAI Y F, CHEN S Y, SHI S R, et al. Effects of different management approaches on the stoichiometric characteristics of soil C, N, and P in a mature Chinese fir plantation[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2020, 723: 137868. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137868. |
| [17] | 庞圣江, 张培, 贾宏炎, 等. 桂西北不同森林类型土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(1): 17-23. |
| PANG S J, ZHANG P, JIA H Y, et al. Research on soil ecological stoichiometry under different forest types in northwest Guangxi[J]. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2015, 31(1): 17-23. | |
| [18] | 庞圣江, 杨保国, 刘士玲, 等. 桂西北喀斯特山区4种森林表土土壤有机碳含量及其养分分布特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2018, 38(4): 60-64+71. |
| PANG S J, YANG B G, LIU S L, et al. The distribution of organic carbon and soil nutrients under four forest types in Karst mountain areas of northwest Guangxi, China[J]. J Central South Univ For & Technol, 2018, 38(4): 60-64,71. DOI: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2018.04.011. | |
| [19] | TIAN H Q, CHEN G S, ZHANG C, et al. Pattern and variation of C∶N∶P ratios in China’s soils: a synthesis of observational data[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2010, 98(1): 139-151. DOI: 10.1007/s10533-009-9382-0. |
| [20] | 杨慧, 朱同彬, 王修华, 等. 云南断陷盆地高原面典型小流域土壤元素含量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(5): 859-865. |
| YANG H, ZHU T B, WANG X H, et al. Soil element contents of typical small watershed in the plateau area of Karst fault basin, Yunnan[J]. Ecol Environ Sci, 2018, 27(5): 859-865. DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2018.05.009. | |
| [21] | YU Y F, HE T G, SONG T Q, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of vegetation successional stages in Karst area of northwest Guangxi[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2018, 49(3): 440-447. DOI: CNKI:SUN:GXNY.0.2018-03-005. |
| [22] | 康冰, 刘世荣, 蔡道雄, 等. 南亚热带不同植被恢复模式下土壤理化性质[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(10): 2479-2486. |
| KANG B, LIU S R, CAI D X, et al. Soil physical and chemical characteristics under different vegetation restoration patterns in China south subtropical area[J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2010, 21(10): 2479-2486. DOI: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.2010.0386. | |
| [23] | 王霖娇, 汪攀, 盛茂银, 等. 西南喀斯特典型石漠化生态系统土壤养分生态化学计量特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(18): 6580-6593. |
| WANG L J, WANG P, SHENG M Y, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil nutrient elements and its influencing factors in typical Karst rocky desertification ecosystems, southwest China[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2018, 38(18): 6580-6593.DOI: 10.5846/stxb201803290635. | |
| [24] | 彭晓, 方晰, 喻林华, 等. 中亚热带4种森林土壤碳、氮、磷化学计量特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2016, 36(11): 65-72. |
| PENG X, FANG X, YU L H, et al. Change characteristic of soil C, N, P stoichiometric ratios in mid-subtropical forests restoration[J]. J Central South Univ For & Technol, 2016, 36(11): 65-72. DOI: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2016.11.012. | |
| [25] | 胡小燕, 段爱国, 张建国, 等. 广西大青山杉木人工林碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4): 1207-1218. |
| HU X Y, DUAN A G, ZHANG J G, et al. Stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus of Chinese fir plantations in Daqing Mountain, Guangxi[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2020, 40(4): 1207-1218. DOI: 10.5846/stxb201812192754. | |
| [26] | 张忠华, 胡刚, 祝介东, 等. 喀斯特森林土壤养分的空间异质性及其对树种分布的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2011, 35(10): 1038-1049. |
| ZHANG Z H, HU G, ZHU J D, et al. Spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients and its impact on tree species distribution in a Karst forest of Southwest China[J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2011, 35(10): 1038-1049. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1258.2011.01038. | |
| [27] | 曾昭霞, 王克林, 刘孝利, 等. 桂西北喀斯特区原生林与次生林鲜叶和凋落叶化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(7): 1907-1914. |
| ZENG Z X, WANG K L, LIU X L, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of live fresh leaves and leaf litter from typical plant communities in a Karst region of northwestern Guangxi, China[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2016, 36(7): 1907-1914. DOI: 10.5846/stxb201409211866. | |
| [28] | TURRIÓN M B, LÓPEZ O, LAFUENTE F, et al. Soil phosphorus forms as quality indicators of soils under different vegetation covers[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2007, 378(1/2):195-198. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.01.037. |
| [29] | 杨慧, 涂春艳, 李青芳, 等. 岩溶区次生林地不同地貌部位土壤C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 南方农业学报, 2015, 46(5): 777-781. |
| YANG H, TU C Y, LI Q F, et al. Analysis of C,N and P stoichiometry of secondary forest in different landforms in Karst area[J]. J South Agric, 2015, 46(5): 777-781. DOI: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2015.5.777. | |
| [30] | 王振宇, 王涛, 邹秉章, 等. 不同生长阶段杉木人工林土壤C∶N∶P化学计量特征与养分动态[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(11):3597-3604. |
| WANG Z Y, WANG T, ZOU B Z, et al. Soil C∶N∶P stoichiometry and nutrient dynamics in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations during different growth stages[J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2020, 31(11):3597-3604. DOI: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202011.005. | |
| [31] | 黄昌勇. 土壤学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 33-49. |
| HUANG C Y. Soil science[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 33-49. | |
| [32] | 贾宇, 徐炳成, 李凤民, 等. 半干旱黄土丘陵区苜蓿人工草地土壤磷素有效性及对生产力的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(1):42-47. |
| JIA Y, XU B C, LI F M, et al. Availability and contributions of soil phosphorus to forage production of seeded alfalfa in semiarid Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2007, 27(1):42-47. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.01.005. | |
| [33] | 吴丽芳, 王妍, 刘云根, 等. 岩溶石漠化区人工植被类型对土壤团聚体生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2021, 49(6): 63-69. |
| WU L F, WANG Y, LIU Y G, et al. Effects of artificial vegetation type on the ecological stoichiometric characteristics of soil aggregates in Karst rocky desertification areas[J]. J Northeast For Univ, 2021, 49(6): 63-69. DOI: 10.13759/j.cnki.dlxb.2021.06.013. | |
| [34] | CLEVELAND C C, LIPTZIN D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass?[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2007, 85(3): 235-252. DOI: 10.1007/s10533-007-9132-0. |
| [35] | 俞月凤, 彭晚霞, 宋同清, 等. 喀斯特峰丛洼地不同森林类型植物和土壤C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(4): 947-954. |
| YU Y F, PENG W X, SONG T Q, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of plant and soil C, N and P in different forest types in depressions between Karst hills, southwest China[J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2014, 25(4): 947-954. DOI: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.2014.0068. | |
| [36] | 刘兴诏, 周国逸, 张德强, 等. 南亚热带森林不同演替阶段植物与土壤中N、P的化学计量特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(1): 64-71. |
| LIU X Z, ZHOU G Y, ZHANG D Q, et al. N and P stoichiometry of plant and soil in lower subtropical forest successional series in southern China[J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2010, 34(1): 64-71. DOI: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2010.01.010. | |
| [37] | 张雨鉴, 王克勤, 宋娅丽, 等. 滇中亚高山5种林型土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(1): 73-82. |
| ZHANG Y J, WANG K Q, SONG Y L, et al. Ecological stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in five forest types in subalpine of middle Yunnan Province[J]. Ecol Environ Sci, 2019, 28(1): 73-82. DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.01.009. | |
| [38] | 朱秋莲, 邢肖毅, 张宏, 等. 黄土丘陵沟壑区不同植被区土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(15): 4674-4682. |
| ZHU Q L, XING X Y, ZHANG H, et al. Soil ecological stoichiometry under different vegetation area on Loess Hillygully Region[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2013, 33(15): 4674-4682. DOI: 10.5846/stxb201212101772. |
| [1] | YANG Hao, LIU Chao, ZHUANG Jiayao, ZHANG Shutong, ZHANG Wentao, MAO Guohao. Effects of different carrier bacterial fertilizers on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and soil nutrients of Amorpha fruticosa [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(3): 81-89. |
| [2] | DING Yong, LIU Xin, ZHANG Jinchi, WANG Yuhao, CHEN Meiling, LI Tao, LIU Xiaowu, ZHOU Yuexiang, SUN Lianhao, LIAO Yi. Effects of acid rain-based transformation on Cunninghamia lanceolata fine root growth and soil nutrient content [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(3): 90-98. |
| [3] | WU Yan, HUANG Qing, LIU Xun, ZHENG Rui, CEN Jiabao, DING Bo, ZHANG Yunlin, FU Yuhong. Effects of Pinus massoniana plantation age on soil physical and chemical properties in Karst areas in southwest China [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(3): 99-107. |
| [4] | HE Kun, WANG Junjie, WANG Benyao, ZHU Haijun, FENG Shucheng. Soil fertility spatial distribution and characteristics of roadside trees in Shanghai [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(3): 164-172. |
| [5] | LI Wei, LI Jiping, ZHANG Yinlong, LI Pingping, HAN Jiangang. Ecological restoration technologies for lake wetlands for carbon peaking and neutrality [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(6): 157-166. |
| [6] | LIU Qingqing, HUANG Zhijun, MA Xiangqing, WANG Zhengning, XING Xianshuang, LIU Bo. Changes of seedling growth and C、N、P stoichiometric characteristics in Chinese fir under shading [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(3): 74-82. |
| [7] | LIU Juntao, ZHONG Jing, LIU Jiming, LUO Shuijing, WANG Mianzhi, FAN Jialin, JIA Liming. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil and leaves in Sapindus mukorossi plantation at an early fruiting stage [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(4): 67-75. |
| [8] | SUN Long, DOU Xu, HU Tongxin. Research progress on the effects of forest fire on forest ecosystem C-N-P ecological stoichiometry characteristics [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(2): 1-9. |
| [9] | LIU Nan, FENG Fujuan, ZHANG Xiuyue. Effects of the litter leaching process by throughfall after clear cutting of primary Pinus koraiensis forest [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(1): 159-167. |
| [10] | GUO Chuanyang, LIN Kaimin, ZHENG Mingming, REN Zhengbiao, LI Mao, ZHENG Hong, YOU Yunfei, CHEN Zhiyun. Short-term effects of thinning on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in a Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(5): 125-131. |
| [11] | ZHAO Jiahao, YUAN Jingxi, YUAN Zaixiang, WANG Xiaomin, CHEN Bin, ZHENG Yuanqing, GUAN Qingwei. An analysis of soil nutrient elements in different terrains of coniferous(Tsuga chinensis var. tchekiangensis) and broadleaf mixed forest in Jiangxi Wuyishan [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(4): 176-182. |
| [12] | HE Bin, LI Qing, FENG Tu, XUE Xiaohui, LI Wangjun, LIU Yong. Variation in leaf functional traits of different-aged Pinus massoniana communities and relationships with soil nutrients [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(2): 181-190. |
| [13] | HAO Yuzhuo, ZHOU Lei, WU Hui,WANG Shuli. Comparison of ecological stoichiometric characteristics of leaf-litter-soil in four types of Fraxinus mandshurica plantations [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2019, 43(04): 101-108. |
| [14] | QIAN Guoping,ZHAO Zhixia, LI Zhengcai,ZHOU Jungang, CHENG Caifang, ZHAO Ruiyu, SUN Jiaojiao. Effects of fire on soil organic carbon in natural secondary forest in north subtropical areas [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2017, 41(06): 115-119. |
| [15] | WANG Xiaomei, KANG Xin, HOU Changying, ZHENG Abao, ZHANG Cunkuan, XU Chi, LIU Maosong. Influence factors of Ilex chinensis seedling regeneration in the mountainous region of southern Jiangsu Province [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2017, 41(04): 197-201. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||