 PDF(2122 KB)
PDF(2122 KB)


Ecological stoichiometry differences in plant-litter-soil across four typical forests of the Luoshan Mountains in Ningxia
YU Yayao, XU Xuelei, LIU Chao, LIU Jiaxing, YANG Tianyu, LI Shuming
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 227-234.
 PDF(2122 KB)
PDF(2122 KB)
 PDF(2122 KB)
PDF(2122 KB)
Ecological stoichiometry differences in plant-litter-soil across four typical forests of the Luoshan Mountains in Ningxia
【Objective】The Luoshan Mountains in the Ningxia Hui Auto nomons Region are unique ecological security barriers in the arid zone of central China. Therefore, the stoichiometric characteristics of this area’s forest ecosystems were studied to describe the limiting nutrients during vegetation development, to provide a theoretical basis for community selection and forest management in this area.【Method】Spruce (Picea crassifolia) forests, Chinese pine (Pinus tabuliformis) forests, aspen (Populus davidiana) forests, and Picea crassifolia × Pinus tabuliformis mixed forests were examined for carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) contents of plant, litter, and soil, and plant-litter-soil ecological stoichiometry correlations were analyzed.【Result】(1) C content of leaves and branches were significantly higher compared with roots, the N and P contents of leaves were significantly higher compared with branches and roots, and leaf C/N was significantly lower compared with branches and roots. Furthermore, leaf and branch N content in Populus davidiana forests were significantly higher, and root N content in Pinus tabuliformis forests were significantly lower, compared with other forests. (2) Litter N, P content, and N/P in Populus davidiana forests were significantly higher, and C/N and C/P were significantly lower, compared with other forests. (3) Soil C, N, P content, C/N, and C/P did not differ significantly among forests, while soil N/P in Picea crassifolia forests was significantly higher than in other forests. (4) Plant N content was significantly positively correlated with litter N content and N/P, and significantly negatively correlated with litter C/N. Plant C/N was significantly positively correlated with litter C content, and strongly negatively correlated with litter N/P. Soil C/N and N/P were significantly positively correlated with plant P content and litter C/P, and significantly negatively correlated with plant C/P. The plant P content was significantly positively correlated with soil pH. Altitude was significantly positively correlated with litter C/N and C/P, and significantly negatively correlated with N content and N/P. Soil N/P was significantly negatively correlated with pH, and significantly positively correlated with altitude and N content. Soil C, N, P content, C/N, and C/P were significantly positively correlated with organic C content.【Conclusion】The plant growth and litter decomposition were both limited by N in the four main forest communities of the Luo Mountains, especially within the coniferous forests. Hence, the protection and use of N elements should be strengthened in these areas. The growth rate is the fastest and litter decomposes more easily in Populus davidiana forests, which are thus candidates for protection and vegetation restoration across the Luoshan Mountains.
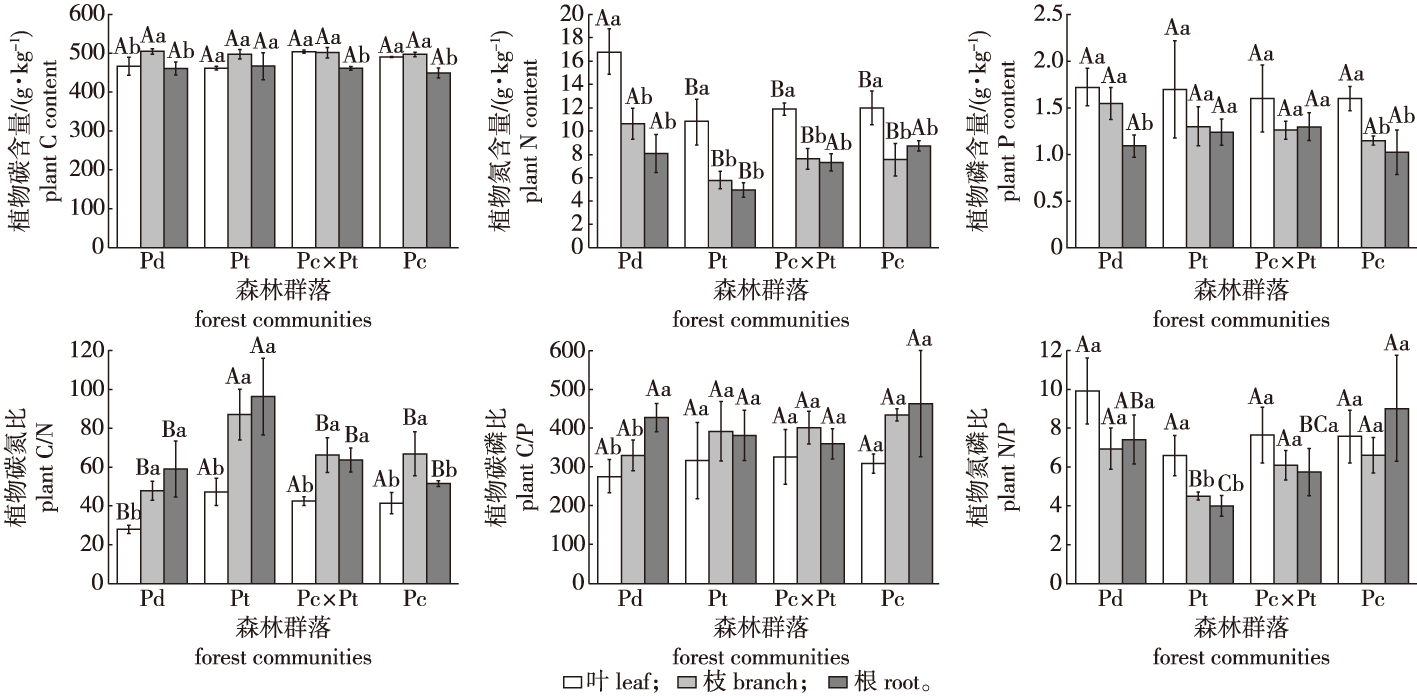
ecological stoichiometry / plant / litter / soil / Luoshan Mountains National Nature Reserve, Ningxia
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
任悦, 高广磊, 丁国栋, 等. 沙地樟子松人工林叶片-枯落物-土壤氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(3):743-750.
|
| [5] |
陈婵, 张仕吉, 李雷达, 等. 中亚热带植被恢复阶段植物叶片、凋落物、土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(8):658-671.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
俞月凤, 何铁光, 曾成城, 等. 喀斯特区不同退化程度植被群落植物-凋落物-土壤-微生物生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(3):935-946.
|
| [8] |
白雪娟, 曾全超, 安韶山, 等. 黄土高原不同人工林叶片-凋落叶-土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(12):3823-3830.
|
| [9] |
施兴文, 刘超, 秦伟春, 等. 宁夏罗山国家级自然保护区野生观赏植物资源调查与分析[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2016(4):93-97.
|
| [10] |
曹兵, 秦伟春. 宁夏罗山森林资源[M]. 银川: 阳光出版社, 2019.
|
| [11] |
郝玉琢, 周磊, 吴慧, 等. 4种类型水曲柳人工林叶片-凋落物-土壤生态化学计量特征比较[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(4):101-108.
|
| [12] |
乔磊磊, 李袁泽, 翟珈莹, 等. 黄土丘陵区植被恢复模式对土壤碳组分的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(5):14-20.
|
| [13] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M].3 版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000:30-177.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
原雅楠, 李正才, 王斌, 等. 不同林龄榧树根、枝、叶的C、N、P化学计量及内稳性特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(6):135-142.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
冀盼盼, 张健飞, 张玉珍, 等. 不同林龄华北落叶松人工林生态化学计量特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(3):126-132.
|
| [20] |
胡耀升, 么旭阳, 刘艳红. 长白山森林不同演替阶段植物与土壤氮磷的化学计量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(3):632-638.
|
| [21] |
姜沛沛, 曹扬, 陈云明, 等. 陕西省3种主要树种叶片、凋落物和土壤N、P化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(2):443-454.
|
| [22] |
马寰菲, 解梦怡, 胡汗, 等. 秦岭不同海拔森林土壤-植物-凋落物化学计量特征对土壤氮组分的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(3):749-757.
|
| [23] |
赵畅, 龙健, 李娟, 等. 茂兰喀斯特原生林不同坡向及分解层的凋落物现存量和养分特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(2):295-303.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
张萍, 章广琦, 赵一娉, 等. 黄土丘陵区不同森林类型叶片-凋落物-土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(14):5087-5098.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
朱育锋, 吴玲, 彭晚霞, 等. 广西不同林龄桉树人工林叶-凋落物-土壤C、N、P生态化学计量特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(6):92-98,106.
|
| [30] |
陆晓辉, 丁贵杰, 陆德辉. 人工调控措施下马尾松凋落叶化学质量变化及与分解速率的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(7):2325-2333.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
姚彩萍, 陈银萍, 李玉强, 等. 北方林草交错带土壤生态化学计量特征及其影响因素[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2022, 42(3):235-243.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |