JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY ›› 2019, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 137-142.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.201902001
Previous Articles Next Articles
LIAO Yangwenke1,2( ), CUI Rongrong2, XIE Yinfeng2
), CUI Rongrong2, XIE Yinfeng2
Received:2019-02-17
Revised:2019-04-10
Online:2019-11-30
Published:2019-11-30
CLC Number:
LIAO Yangwenke, CUI Rongrong, XIE Yinfeng. The role of β-cyanoalanin synthase in polar leaves under salt stress[J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2019, 43(6): 137-142.
Table 1
Primers used in this study for qPCR tests"
| 基因 genes | 编码蛋白 encoding protein | 基因编号 accession No | 引物序列 primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ptr 18S | 18S核糖体DNA 18S rDNA | AY652861.1 | F. 5'-TCGTCCCTTCTACCGGCGAT-3' R. 5'-CTCCGATCCCGAAGGCCAAC -3' |
| ACS7 | ACC合成酶 1-aminocyclopropane-1- carboxylate (ACC) synthase | Potri.003G132300.1 | F. 5'-GGATGTCGACACCAAGAAGCC-3' R. 5'-GGGCGATTGAGGTATGGGAGA-3' |
| ACO3 | ACC氧化酶 1-aminocyclopropane-1- carboxylate (ACC) oxidase 3 | Potri.014G159000.1 | F. 5'-CCTTTGGCACCAAGGTCAGC-3' R. 5'-GGCCATCCTTGAGAAGCTGGA-3' |
| CYS C1 | β-氰丙氨酸合酶 β-cyanoalanine synthase | Potri.002G160800.1 | F. 5'-CTGGCCCTGAAATATGGGAGGA-3' R. 5'-CTCTCAGCAGGCTCAACTCCA-3' |
| NIT4 | 腈水解酶 nitrilase | Potri.004G199600.1 | F. 5'-GGGTGTGATTGAGAGGGAGGGATA-3' R. 5'-CCGGAATCGTTGATCCATCTCCA-3' |
| AOX1b | 交替呼吸氧化酶 alternative oxidase 1b | Potri.003G103900.1 | F. 5'-TGCATTGCAAATCACTACGA-3' R. 5'-AGCAAATACAAGGGCTCGTT-3' |
| COX6b | 细胞色素c氧化酶 cytochromec oxidase 6b | Potri.005G162100.1 | F. 5'-ACCAGCTGATTACCGATTCC-3' R. 5'-CACTAGGGCAGAGTGAACGA-3' |
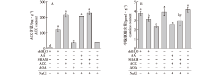
Fig.2
Effects of chemical pretreatments on ACC and cysteine content in poplar leaves under salt stress The chemicals shown beyond the black solid line were applied for pretreatment. “+” represents the presence and “-” indicates the absence of selected chemical in the treatment. The same below."

| [1] |
BLEECKER A B, KENDE H. Ethylene: a gaseous signal molecule in plants[J]. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 2000, 16(1):1-18. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.1.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.1 |
| [2] |
CAO W H, LIU J, HE X J, et al. Modulation of ethylene responses affects plant salt-stress responses[J]. Plant Physiol, 2007, 143(2):707-719. DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.094292.
doi: 10.1104/pp.106.094292 |
| [3] |
VAHALA J, RUONALA R, KEINÄNEN M, et al. Ethylene insensitivity modulates ozone-induced cell death in birch[J]. Plant Physiol, 2003, 132(1):185-195. DOI: 10.1104/pp.102.018887.
doi: 10.1104/pp.102.018887 |
| [4] |
WANG H H, LIANG X L, WAN Q, et al. Ethylene and nitric oxide are involved in maintaining ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis callus under salt stress[J]. Planta, 2009, 230(2):293-307. DOI: 10.1007/s00425-009-0946-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-0946-y |
| [5] | PEISER G D, WANG T T, HOFFMAN N E, et al. Formation of cyanide from carbon 1 of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid during its conversion to ethylene[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1984, 81(10) 3059-3063. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3059. |
| [6] | SIEGIEN I, BOGATEK R. Cyanide action in plants-from toxic to regulatory[J]. Acta Physiolo Plant, 2006, 28(5):483-497. DOI: 10.1007/bf02706632. |
| [7] |
ÁLVAREZ C, GARCIA I, ROMERO L C, et al. Mitochondrial sulfide detoxification requires a functional isoform O-acetylserine(thiol)lyase C in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Molecular Plant, 2012, 5(6):1217-1226. DOI: 10.1093/mp/sss043.
doi: 10.1093/mp/sss043 |
| [8] |
PIOTROWSKI M. Primary or secondary? Versatile nitrilases in plant metabolism[J]. Phytochemistry, 2008, 69(15):2655-2667. DOI: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.08.020.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.08.020 |
| [9] |
HATZFELD Y, MARUYAMA A, SCHMIDT A, et al. beta-Cyanoalanine synthase is a mitochondrial cysteine synthase-like protein in spinach and Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiol, 2000, 123(3):1163-1172. DOI: 10.1104/pp.123.3.1163.
doi: 10.1104/pp.123.3.1163 |
| [10] |
WATANABE M, KUSANO M, OIKAWA A, et al. Physiological roles of the β-substituted alanine synthase gene family in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiol, 2008, 146(1):310-320. DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.106831.
doi: 10.1104/pp.107.106831 |
| [11] | 余璐璐, 曹中权, 刘龙山, 等. 盐芥CAS基因的生物信息学分析及在盐胁迫下的表达[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(7):25-29. DOI: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302,2015,07,007.43. |
| [12] |
DA SILVA C J, BATISTA FONTES E P, MODOLO L V. Salinity-induced accumulation of endogenous H2S and NO is associated with modulation of the antioxidant and redox defense systems in Nicotiana tabacum L. cv. Havana[J]. Plant Science, 2017, 256:148-159. DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.12.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.12.011 |
| [13] |
GARCÍA I, ROSAS T, BEJARANO E R, et al. Transient transcriptional regulation of the CYS-C1 gene and cyanide accumulation upon pathogen infection in the plant immune response[J]. Plant Physiol, 2013, 162(4):2015-2027. DOI: 10.1104/pp.113.219436.
doi: 10.1104/pp.113.219436 |
| [14] | CHIVASA S, CARR J P. Cyanide restores N gene-mediated resistance to tobacco mosaic virus in transgenic tobacco expressing salicylic acid hydroxylase[J]. Plant Cell, 1998, 10(9):1489-1498. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.10.9.1489. |
| [15] |
CHIVASA S, MURPHY A M, NAYLOR M, et al. Salicylic acid interferes with tobacco mosaic virus replication via a novel salicylhydroxamic acid-sensitive mechanism[J]. Plant Cell, 1997, 9(4):547-557. DOI: 10.1105tpc.9.4.547.
doi: 10.2307/3870506 |
| [16] |
WANG H H, LIANG X L, HUANG J J, et al. Involvement of ethylene and hydrogen peroxide in induction of alternative respiratory pathway in salt-treated Arabidopsis calluses[J]. Plant and Cell Physiol, 2010, 51(10):1754-1765. DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcq134.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcq134 |
| [17] |
JANSSON S, DOUGLAS C J. Populus: A model system for plant biology[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2007, 58(1):435-458. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103956.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103956 |
| [18] |
LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2ΔΔct Tmethod[J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4):402-408. DOI: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 |
| [19] |
LIZADA M C, YANG S F. A simple and sensitive assay for 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1979, 100(1):140-145. DOI: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90123-4.
doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90123-4 |
| [20] |
GAITONDE M K. A spectrophotometric method for the direct determination of cysteine in the presence of other naturally occurring amino acids[J]. The Biochem J, 1967, 104(2):627-633. DOI: 10.1042/bj1040627.
doi: 10.1042/bj1040627 |
| [21] |
TAKÁCS Z, POÓR P, TARI I. Comparison of polyamine metabolism in tomato plants exposed to different concentrations of salicylic acid under light or dark conditions[J]. Plant Physiol Biochem, 2016, 108:266-278. DOI: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.07.020.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.07.020 |
| [22] |
KHAN M M, ISLAM E, IREM S, et al. Pb-induced phytotoxicity in para grass (Brachiaria mutica) and Castorbean (Ricinus communis L.): antioxidant and ultrastructural studies[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 200:257-265. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.101.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.101 |
| [23] | WANG H H, HUANG J J, BI Y R. Induction of alternative respiratory pathway involves nitric oxide, hydrogen peroxide and ethylene under salt stress[J]. Plant Signaling &Behavior, 2010, 5(12):1636-1637. DOI: 10.4161/psb.5.12.13775. |
| [24] |
ZHU L, LI Y M, LI L, et al. Ethylene is involved in leafy mustard systemic resistance to Turnip mosaic virus infection through the mitochondrial alternative oxidase pathway[J]. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol, 2011, 76(3/4):166-172. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2011.09.005.
doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2011.09.005 |
| [25] | LI Z G. Analysis of some enzymes activities of hydrogen sulfide metabolism in plants[M]//CADENAS E, PACKER L. Hydrogen sulfide in redox biology. Pt B. San Diego: Elsevier Academic Press Inc, 2015: 253-269. DOI: 10.1016/bs.mie.2014.11.035. |
| [26] |
GARCÍA I, CASTELLANO J M, VIOQUE B, et al. Mitochondrial β-cyanoalanine synthase is essential for root hair formation in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant Cell, 2010, 22(10):3268-3279. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.110.076828.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.076828 |
| [27] | MØLLER I M. Plant mitochondria and oxidative stress: Electron transport, NADPH turnover, and metabolism of reactive oxygen species[J]. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant & MolBiol, 2001, 52(1):561-591. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.561. |
| [28] |
WAGNER A M, MOORE A L. Structure and function of the plant alternative oxidase: its putative role in the oxygen defence mechanism[J]. Bioscience Reports, 1997, 17(3):319-333. DOI: 10.1023/a:1027388729586.
doi: 10.1023/A:1027388729586 |
| [1] | XU Huihui, BAN Zhuo, WANG Chenxue, BI Quanxin, LIU Xiaojuan, WANG Libing. The identification and functional analysis of BZR1 genes in yellowhorn [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2025, 49(2): 12-22. |
| [2] | SONG Zihe, ZHEN Yan. Advancements in the research of miRNAs associated with plant drought and salt stress responses [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(4): 1-11. |
| [3] | ZONG Jianwei, LI Cheng, ZHANG Jing, YANG Yuhua. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and physiological characteristics of Xanthoceras sorbifolium under salt stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(4): 168-176. |
| [4] | LU Zhiguo, HUA Jianfeng, YIN Yunlong, SHI Qin. Effects of nitrogen form on growth and physiological characteristics of Hibiscus hamabo under salt stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(3): 91-98. |
| [5] | MA Shilin, CAO Pengxiang, ZHANG Jinchi, LIU Jing, WANG Jinping, ZHU Lingjun, YUAN Zhongming. Effects of AMF on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Zelkova serrata under salt stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(1): 122-130. |
| [6] | SHE Jianwei, ZHANG Kang, ZHENG Xu, ZHAO Xiaojun, CHENG Fang, TANG Luozhong. Effects of seawater on growth and physiology of Betula microphylla var. paludosa cutting seedlings [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(5): 102-108. |
| [7] | HUA Weicheng, TIAN Jiarong, SUN Xinyu, XU Yannan. Assessing the stem taper function and volume estimation of poplar (Populus) by terrestrial laser scanning [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(4): 41-48. |
| [8] | LI Mengjuan, ZHU Liming, HUO Junnan, ZHANG Jingbo, SHI Jisen, CHENG Tielong. Cloning and expression analyses of NtCBL1,NtCBL2 gene of Nitraria tangutorum [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(3): 93-99. |
| [9] | CUI Lingjun, LIU Yuxia, LIN Jian, SHI Kaiming. Effects of AMF on photosynthetic characteristics of Phoebe zhennan under salt stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(1): 101-106. |
| [10] | YE Zhalong, YAN Bin, SHEN Tingting, NING Kun, LI Huiyu. Analysis of salt tolerance in BpmiR156 overexpression Betula platyphylla [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(6): 147-151. |
| [11] | LU Qiang, YANG Ling, WANG Haowei, YUAN Jiaqiu, FU Xiangxiang, FANG Yan. Responses of photosynthetic characteristics and chloroplast ultrastructure to salt stress in seedlings of Cornus hongkongensis subsp. elegans [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(4): 29-36. |
| [12] | CUI Lingjun, LIU Yuxia, LIN Jian, SHI Kaiming. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on roots growth and endogenous hormones of Phoebe zhennan under salt stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(4): 119-124. |
| [13] | WANG Haowei, YANG Ling, LU Qiang, FU Xiangxiang. Effects of salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Cornus florida [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(3): 89-94. |
| [14] | ZHANG Heng, LIU Xiaoting, CHEN Song, ZHOU Xueyan, SI Dongjing, LI Ying, ZHAO Xiyang. Analysis of differentially expressed proteins in leaves of triploid Populus simonii × P. nigra hybrid clones under salt stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(2): 59-66. |
| [15] | ZHAO Xiaojun, CHENG Fang, ZHANG Kang, HUANG Kaidong, NI Yun, MENG Xiao, TANG Luozhong. Root morphology of different poplar clone stecklings under waterlogging and flooding treatment [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2019, 43(5): 1-8. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||