 PDF(1775 KB)
PDF(1775 KB)


An evaluation on the cold tolerance of twenty-three Cyclocarya paliurus families under natural low temperatures
ZHANG Zanpei, GU Yueying, SHANG Xulan, WANG Ji, FANG Shengzuo
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 85-92.
 PDF(1775 KB)
PDF(1775 KB)
 PDF(1775 KB)
PDF(1775 KB)
An evaluation on the cold tolerance of twenty-three Cyclocarya paliurus families under natural low temperatures
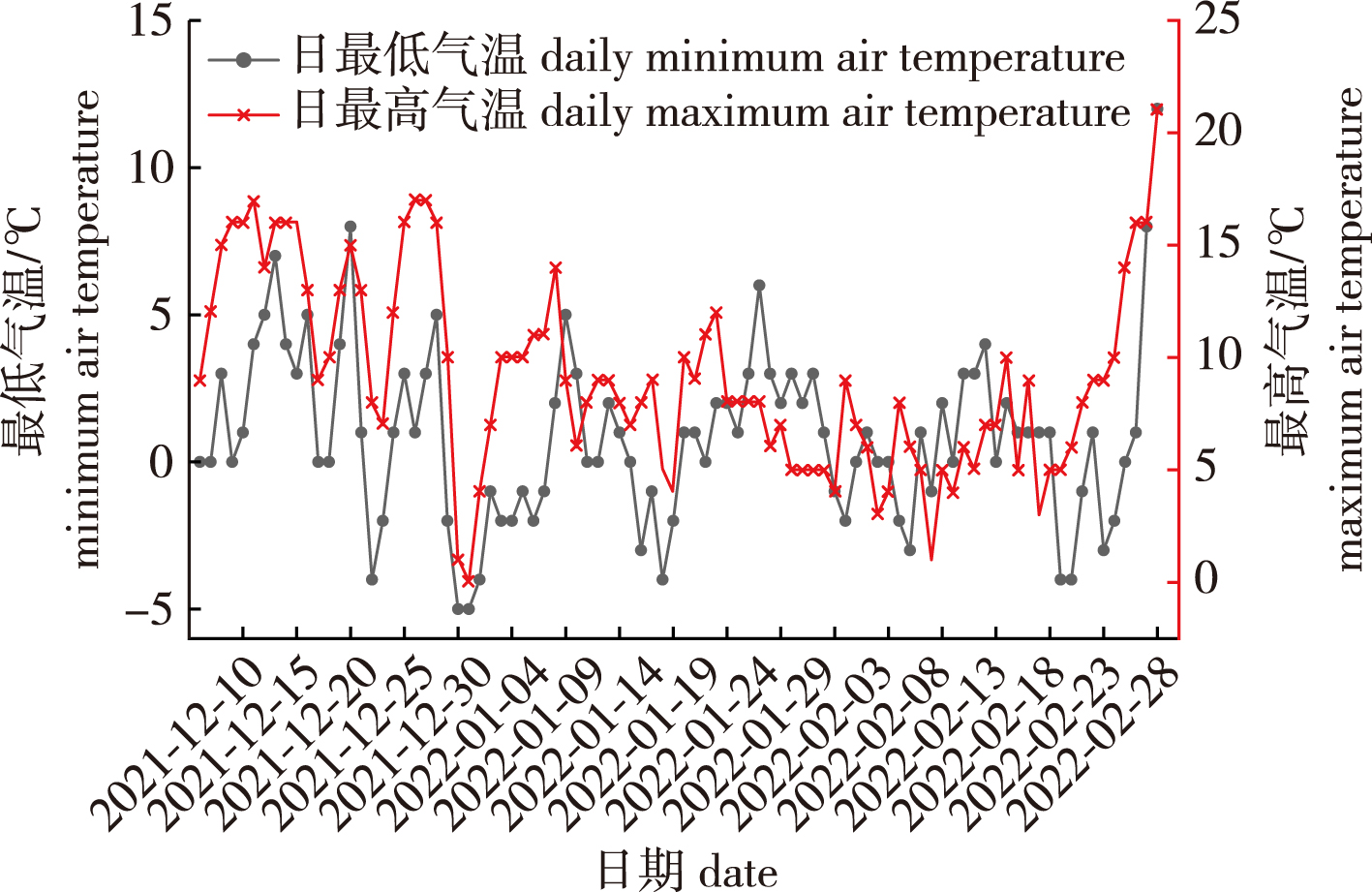
【Objective】To provide a theoretical basis for the introduction, selective breeding, and cultivation of Cyclocarya paliurus, the cold resistance of different families of C. paliurus under natural low temperature stress was evaluated.【Method】Using the current branches of C. paliurus from 23 families as materials, the relative electric conductivity (REC), malondialdehyde (MDA) content, peroxidase (POD) activity, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, soluble sugar (SS), soluble protein (SP), starch (ST) and free proline (Pro) content were determined after natural low temperature stress. A preliminary evaluation of the cold resistance of C. paliurus families was conducted through a principal component analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis.【Result】After natural low temperature stress, there were significant differences in the REC, MDA, POD and SOD activity, SS, SP, ST and Pro content among the current branches of the 23 families. The PCA found that the four principal components represented 72.4% of the information regarding the various physiological indicators. A cluster analysis showed that the cold resistance of 23 families could be divided into three categories based on the comprehensive score of the PCA for each family. The first category included only two families (SCMC31 and ZJTTS2) with the good cold resistance, and the compositive score ranging from 1.208 to 1.284. The second category indude 17 families (including GZSQ12, GXBS12, ZJFYS6, AHQLF8 and HBWF10) that exhibited moderate cold resistance, with composite scores ranging from -0.343 to 0.631. The third category included four families (GZSQ9, ZJTTS3, SCMC22, and SCMC30) with poor cold tolerance, with composite scores ranging from -1.259 to -0.745.【Conclusion】After natural low temperature stress, significant differences in the measured physiological indices were observed between the current branches of C. paliurus from different families (P < 0.05). Based on the PCA and cluster analysis results, there were different cold resistances among the 23 Cyclocarya paliurus families, which could be divided into three categories. The results not only provide a basis for an in-depth study of the cold tolerate mechanism of C. paliurus, but also for future screening of the cold tolerate genotypes of C. paliurus.
Cyclocarya paliurus / family / low temperature stress / principal component analysis(PCA) / physiological indicators / overall evaluation
| [1] |
谢明勇, 谢建华. 青钱柳研究进展[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2008, 27(1):113-121.
|
| [2] |
方升佐, 洑香香. 青钱柳资源培育与开发利用的研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(1):95-100.
|
| [3] |
舒任庚, 徐昌瑞, 黎莲娘. 青钱柳甜味成分的研究[J]. 药学学报, 1995, 30(10):757-761.
|
| [4] |
钟瑞建, 高幼衡, 徐昌瑞, 等. 青钱柳中五环三萜成分的研究[J]. 中草药, 1996, 27(7):387-388.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
权威, 薛文通, 赵天瑶, 等. 植物对低温胁迫的响应机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2023, 28(2):14-22.
|
| [10] |
刘紫烟, 刘佳乐, 朱圆圆, 等. 木本植物低温应答机制研究进展[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(2):157-163.
|
| [11] |
牟开萍, 李维芳, 杨文新, 等. 20个月季品种的抗寒性综合评价[J]. 草原与草坪, 2021, 41(6):58-66.
|
| [12] |
刘钰玺, 陈佰鸿, 马宗桓, 等. 河西走廊酿酒葡萄砧木抗寒性综合评价[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2020, 55(6):86-96.
|
| [13] |
何伟, 艾军, 范书田, 等. 葡萄品种及砧木抗寒性评价方法研究[J]. 果树学报, 2015, 32(6):1135-1142.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
赵世杰, 许长成, 邹琦, 等. 植物组织中丙二醛测定方法的改进[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1994, 30(3):207-210.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000:196-197.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
徐亚军, 赵龙飞, 邢鸿福, 等. 内生细菌对盐胁迫下小麦幼苗脯氨酸和丙二醛的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(11):3726-3737.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
李晓龙, 褚燕南, 张磊, 等. 苹果花期抗寒能力判定指标解析[J]. 果树学报, 2022, 39(10):1935-1944.
|
| [31] |
张博, 刘立强, 秦伟, 等. 新疆野苹果抗寒生理生化机制研究[J]. 经济林研究, 2021, 39(4):60-68.
|
| [32] |
韩立群, 马凯, 丁军伟, 等. 低温处理下新疆野生核桃的生理响应及抗寒性评价[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2019, 34(5):98-101,126.
|
| [33] |
吴硕, 贾彦丽, 智福军. 低温胁迫下核桃枝条抗寒性综合评价[J]. 林业与生态科学, 2020, 35(3):314-319.
|
| [34] |
王一峰, 赵淑玲, 王瀚, 等. 不同核桃种质展叶期抗寒性的综合评价[J]. 经济林研究, 2019, 37(1):50-60.
|
| [35] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |