 PDF(2610 KB)
PDF(2610 KB)


Research on TLS single tree detection method based on point cloud slicing combined with clustering algorithm
YI Jing, MA Kaisen, XIANG Jianping, TANG Jie, JIANG Fugen, CHEN Song, SUN Hua
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 113-122.
 PDF(2610 KB)
PDF(2610 KB)
 PDF(2610 KB)
PDF(2610 KB)
Research on TLS single tree detection method based on point cloud slicing combined with clustering algorithm
【Objective】To solve the problem that a canopy height model (CHM) and normalized point cloud (NPC) directly generated by terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) are not capable of detecting individual trees in complex stands, this study introduced the method of point cloud slicing combined with clustering to improve the detection accuracy.【Method】In this study, six sample plots in a plantation with different stand densities in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China, were used as the research objects. First, the NPC data of a sample plot obtained by TLS were used to extract point cloud slices at a height of 1.3 m, and then the density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) and mean shift algorithms were used to cluster the tree trunk point clouds in the slices. The accuracy was verified by the field survey data, and the detection results were compared with those of the local maximum algorithm based on a CHM, and a point cloud segmentation algorithm based on an NPC. The applicability and parameter sensitivity of the different detection methods were evaluated and analyzed.【Result】Satisfactory detection results were obtained by all methods, and the optimal detection accuracy F-score was ≥ 0.86 for each sample plot. The individual tree detection method using point cloud slicing combined with a clustering algorithm produced better results. The clustering threshold epsilon neighborhood (Eps) value of the DBSCAN algorithm and the clustering radius r of the mean shift algorithm significantly affected the individual tree detection rate, with the maximum Eps depending on the maximum stand spacing and optimum results when r was close to the maximum individual tree diameter at breast height.【Conclusion】Individual tree detection based on point cloud slicing combined with a clustering algorithm can increase the detection rate of understory trees lower forest, effectively improve the accuracy of single tree detection in dense stands, and provide a reference for the selection of single tree detection methods in different forest stands.
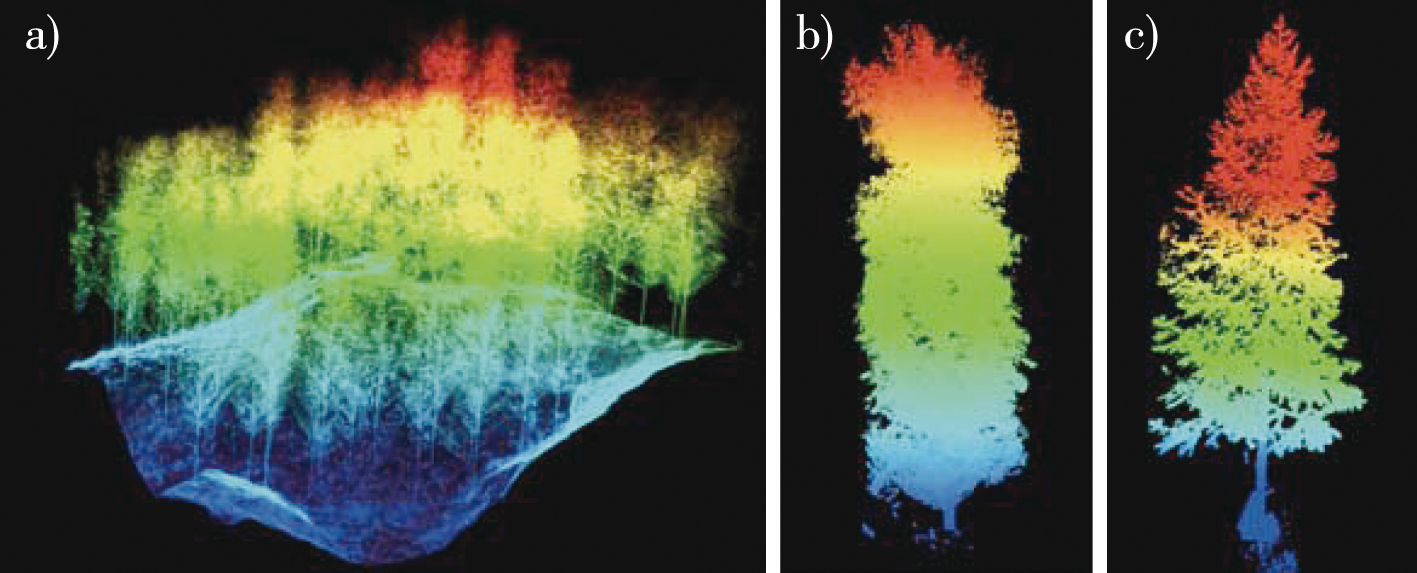
terrestrial laser scanning / single tree detection / point cloud slicing / clustering algorithm / extraction of forest parameters / plantation
| [1] |
曹林, 佘光辉, 代劲松, 等. 激光雷达技术估测森林生物量的研究现状及展望[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 37(3):163-169.
|
| [2] |
李增元, 刘清旺, 庞勇. 激光雷达森林参数反演研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2016, 20(5):1138-1150.
|
| [3] |
吴楠, 李增元, 廖声熙, 等. 国内外林业遥感应用研究概况与展望[J]. 世界林业研究, 2017, 30(6):34-40.
|
| [4] |
刘鲁霞, 庞勇. 机载激光雷达和地基激光雷达林业应用现状[J]. 世界林业研究, 2014, 27(1):49-56.
|
| [5] |
花伟成, 田佳榕, 孙心雨, 等. 基于TLS数据的杨树削度方程建立及材积估算[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(4):41-48.
|
| [6] |
蒋佳文, 温小荣, 顾海波, 等. 基于多站扫描的点云特征参数与材积结构动态分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(6):83-90.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
刘会玲, 张晓丽, 张莹, 等. 机载激光雷达单木识别研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(8):40-48.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
刘方舟, 刘浩, 云挺. 基于分水岭优化思想的单木信息分割算法[J]. 林业工程学报, 2020, 5(5):109-116.
|
| [11] |
郭庆华, 刘瑾, 陶胜利, 等. 激光雷达在森林生态系统监测模拟中的应用现状与展望[J]. 科学通报, 2014, 59(6):459-478.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
林秀云, 孙圆, 刘晨曦, 等. 依据地面激光扫描数据的杉木材积建模与造材[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2022, 50(1):33-39.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
麻卫峰, 王金亮, 麻源源, 等. 改进K均值聚类的点云林木胸径提取[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(9):122-129.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
朱德海. 点云库PCL学习教程[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2012:189-191.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
李响, 甄贞, 赵颖慧. 基于局域最大值法单木位置探测的适宜模型研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(3):27-33.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
杨海城. 基于ULS和TLS的天然次生林不同林层单木参数估测及对比[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2021.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |