JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY ›› 2023, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 9-17.doi: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202110038
Special Issue: “攥紧中国种子”视域下的中国林草种业研究专题Ⅰ
Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Miao1( ), GAO Handong1,*(
), GAO Handong1,*( ), GAO Yan2, XUE Xiaoming3
), GAO Yan2, XUE Xiaoming3
Received:2021-10-18
Revised:2022-05-23
Online:2023-03-30
Published:2023-03-28
CLC Number:
LIU Miao, GAO Handong, GAO Yan, XUE Xiaoming. Study on the physiological and biochemical changes of Phoebe sheareri seed during its dormancy breaking[J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(2): 9-17.
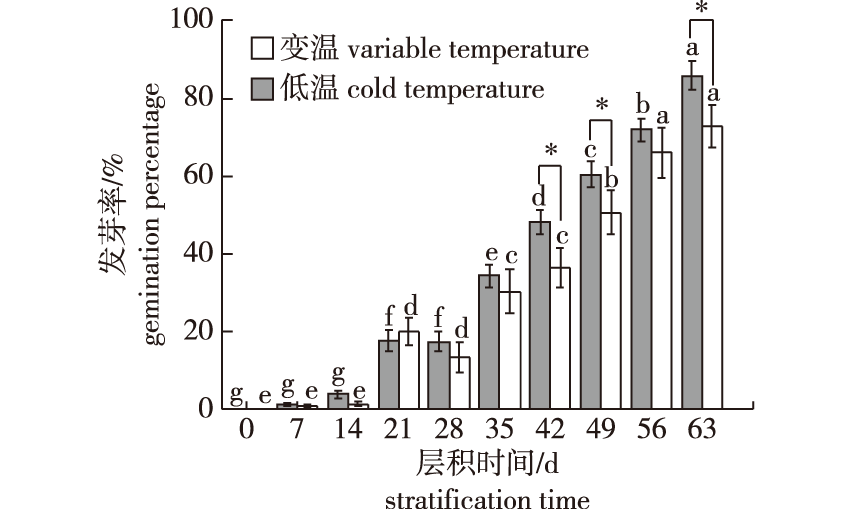
Fig.1
The germination percentage of Phoebe sheareri seeds treated with different stratification treatments Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different stratification time of the same treatment(P<0.05). *indicates significant differences between different treatments at the same stratification time(P<0.05). The same below."
| [1] | 陆云峰, 王豪, 徐沁怡, 等. 樟科楠属4种植物种实表型性状及其发芽特性研究[J]. 种子, 2020, 39(12): 107-112,119. |
| LU Y F, WANG H, XU Q Y, et al. Study on the Phenotypic characters and germination Characteristics of four Lauraceae Phoebe plants[J]. Seed, 2020, 39(12): 107-112,119. DOI:10.16590/j.cnki.1001-4705.2020.12.107. | |
| [2] | 李珍, 王素娟, 刘纯玲, 等. 紫楠及浙江楠种子萌发特性研究[J]. 北方园艺, 2012(7): 58-60. |
| LI Z, WANG S J, LIU C L, et al. Study on seed germination characteristics of Phoebe sheareri and Phoebe chekiangensis[J]. North Hortic, 2012(7): 58-60. | |
| [3] | 刘虎, 刘敏, 汤雯, 等. 紫楠木材的构造特征[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2017, 45(2):53-56. |
| LIU H, LIU M, TANG W, et al. Wood structural characteristics of Phoebe sheareri[J]. J Northeast For Univ, 2017, 45(2):53-56. DOI: 10.13759/j.cnki.dlxb.2017.02.011. | |
| [4] | 李军, 陆云峰, 杨安娜, 等. 紫楠天然群落物种多样性对不同干扰强度的响应[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(2): 279-288. |
| LI J, LU A N, YANG A N, et al. Species diversity of natural Phoebe sheareri communities with different disturbance intensities[J]. J Zhejiang A & F Univ, 2019, 36(2): 279-288. | |
| [5] | 贾贤, 黄秋生, 刘光华, 等. 我国楠木资源的研究现状[J]. 中国园艺文摘, 2014, 30(10): 55-59. |
| JIA X, HUANG Q S, LIU G H, et al. Research status of Phoebe resources in China[J]. Chin Hortic Abstr, 2014, 30(10): 55-59. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0873.2014.10.023. | |
| [6] | 史晓华, 田丽洁, 史忠礼. 紫楠种子休眠生理的研究[J]. 种子, 1983, 33(1): 32-33. |
| SHI X H, TIAN L J, SHI Z L. Studies on dormancy physiology of seeds of Phoebe sheareri[J]. Seed, 1983, 33(1): 32-33. DOI: 10.16590/j.cnki.1001-4705.1988.01.045. | |
| [7] | 李珍. 不同基质配比及施肥配方对紫楠、浙江楠容器苗生长的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2012. |
| LI Z. The effect of different substrate compositions and fertilizer formulations on Phoebe sheareri and Phoebe chekiangensis container seedlings[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University, 2012. | |
| [8] | 王小丽. 不同预处理对紫楠种子萌发的影响[J]. 现代园艺, 2018(7): 37-39,178. |
| WANG X L. Effects of different pretreatment on seed germination of Phoebe sheareri[J]. Modern Hortic, 2018(7): 37-39, 178. DOI: 10.14051/j.cnki.xdyy.2018.07.016. | |
| [9] | 许世达, 王立, 吴莹, 等. 低温层积对3种椴树属植物种子活性氧含量和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2022, 31(6):84-86. |
| XU S D, WANG L, WU Y, et al. Effect of low temperature stratification on reactive oxygen species content and antioxidant enzyme activities in seeds of three species of Tilia Linn[J]. J Plant Resour Environ, 2022, 31(6):84-86.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2022.06.09. | |
| [10] | 国家质量技术监督局. 林木种子检验规程: GB 2772—1999[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2000. |
| The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. Rules for forest tree seed testing: GB 2772—1999[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2000. | |
| [11] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. |
| LI H S. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. | |
| [12] | 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. |
| GAO J F. Experimental guidance for plant physiology[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. | |
| [13] | 宋松泉. 种子生物学研究指南[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005. |
| SONG S Q. Guide to seed biology research[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005. | |
| [14] | YANG J C, ZHANG J H, WANG Z Q, et al. Hormonal changes in the grains of rice subjected to water stress during grain filling[J]. Plant physiology, 2001, 127(1): 315-323. DOI: 10.1104/PP.127.1.315. |
| [15] | YANG Y M, XU C N, WANG B M, et al. Effects of plant growth regulators on secondary wall thickening of cotton fibres[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2001, 35(3): 233-237. DOI: 10.1023/A:1014442015872. |
| [16] | JUNTTILA O. The mechanism of low temperature dormancy in mature seeds of Syringa species[J]. Physiologia Plant, 2010, 29(2): 256-263. |
| [17] | 洑香香, 周晓东, 刘红娜. 山茱萸种子休眠机理与解除方法初探[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2013, 33(4): 7-12. |
| FU X X, ZHOU X D, LIU H N. A preliminary study on seed dormancy mechanism and relieving methods in Cornus officinalis[J]. J Central South Unive of For & Techno, 2013, 33(4): 7-12. DOI: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923.2013.04.011. | |
| [18] | ZHOU Z Q, BAO W K. Changes in seed dormancy of Rosa multibracteata Hemsl and E.H. Wilson with increasing elevation in an arid valley in the eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Ecological Research, 2014, 29(4): 693-700. DOI: 10.1007/s11284-014-1155-0. |
| [19] | KHAN A A, ZENG G W. Compensatory energy processes controlling dormancy and germination[J]. Plant physiology, 1984, 75(1):68. |
| [20] | 赵婕, 张子晗, 侯秋彦, 等. 东京野茉莉种子休眠特性的研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(1): 45-51. |
| ZHAO J, ZHANG Z H, HOU Q Y, et al. Investigation on dormancy characteristics of Styrax tonkinensis seeds[J]. J Central South Univ of Fore & Techno, 2019, 39(1): 45-51. DoI: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2019.01.008. | |
| [21] | 王家源, 方升佐. 青钱柳种子层积过程中贮藏物质含量及酶活性的变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 42(1): 111-113. |
| WANG J Y, FANG S Z. Storage substance content and corresponding enzyme activity during the stratification of Cyclocarya paliurus seeds[J]. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2007, 42(1): 111-113. | |
| [22] | 祝遵凌, 林庆梅, 许园园. 欧洲鹅耳枥种子层积过程中贮藏物质及酶活性的变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 37(6): 157-160. |
| ZHU Z L, LIN Q H, XU Y Y. Storage substance content and corresponding enzyme activity during the stratification of Carpinus betulus seeds[J]. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2013, 37(6): 157-160. | |
| [23] | 汪源, 刘光立, 张倩, 等. 层积处理对四川牡丹种子生理生化特性的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2013(24): 59-62. |
| WANG Y, LIU G L, ZHANG Q, et al. Effects of stratification treatment on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Paeonia decomposita seed[J]. North Hortic, 2013(24): 59-62. | |
| [24] | 孙海燕, 李强, 朱铭玮, 等. 油用牡丹‘凤丹’种子层积过程中营养物质的代谢变化研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1): 70-78. |
| SUN H Y, LI Q, ZHU M W, et al. Dynamic changes of nutrients of Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ seed during its dormancy breaking[J]. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2021, 45(1): 70-78. | |
| [25] | 彭方仁, 郭娟, 徐柏森. 木本植物营养贮藏蛋白质研究进展[J]. 植物学通报, 2001(4): 445-450. |
| PENG F R, GUO J, XU B S. Progresses of research on vegetative storage proteins in woody plants[J]. Chin Bull Bot, 2001(4): 445-450. | |
| [26] | 龙汉利, 罗建勋, 辜云杰, 等. 桢楠种子萌发过程中抗氧化酶及贮藏物质的变化[J]. 西南农业学报, 2013, 26(3): 978-981. |
| LONG H L, LUO J X, GU Y J, et al. Changes of antioxidant enzymes and storage substance during Phoebe seed germination[J]. Southwest Chin J Agri Sci, 2013, 26(3): 978-981. DOI: 10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2013.03.080. | |
| [27] | 李富恒, 吴晶晶, 赵恒田, 等. 层积前GA处理对老山芹种胚发育及物质代谢的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2020, 51(11): 40-51. |
| LI F H, WU J J, ZHAO H T, et al. Effect of GA treatment on embryo development and material metabolism of Heracleum dissectum Ledeb before stratifications[J]. J Northeast Agri Univ, 2020, 51(11): 40-51. DOI:10.19720/j.cnki.issn.1005-9369.2020.11.05 | |
| [28] | 陈丽培, 沈永宝. 油松种子萌发初始阶段物质代谢的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2010, 32(2): 69-73. |
| CHEN L P, SHEN Y B. Material metabolism of Pinus tabulaeformis seeds during initial germinating stage[J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2010, 32(2): 69-73. DOI: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.2010.02.016. | |
| [29] | 周光宇. 有关同工酶分析的几个问题[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1983(1): 1-4,9. |
| ZHOU G Y. Several problems concerning isozyme analysis[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 1983(1): 1-4,9. DOI: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.1983.01.001. | |
| [30] | 刘雅帅. 山茱萸种子休眠机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2008. |
| LIU Y S. Studies on dormancy mechanism of Macrocarpium officinale seeds[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2008. | |
| [31] | 李戈, 唐玲, 王艳芳, 等. 不同层积条件下滇重楼种子的生理变化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(7): 149-153. |
| LI G, TANG L, WANG Y F, et al. Effect of Different stratification treatment on physiological characteristics of Paris polyphylla Smith var. yunnanensis seed[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(7): 149-153. | |
| [32] | ANNE F. Systems and approaches to studying dormancy: introduction to the workshop[J]. Hortisciene, 1999, 34(7): 1172-1173. |
| [33] | 金雅琴, 李冬林, 黄雪方. 梾木种子低温层积过程中内源激素含量的动态变化特征[J]. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(11): 2255-2261. |
| JIN Y Q, LI D L, HUANG X F. Dynamic variation characteristic of endogenous hormone content in Cornus macrophylla seeds during cold Stratification[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2014, 34(11): 2255-2261. | |
| [34] | 于敏, 徐恒, 张华, 等. 植物激素在种子休眠与萌发中的调控机制[J]. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(5): 599-606. |
| YU M, XU H, ZHANG H, et al. Regulation of plant hormones on seed dormancy and germination[J]. Plant Physiology Journal 2016, 52(5): 599-606. DOI: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2016.0061. | |
| [35] | 张俊杰, 韦霄, 柴胜丰, 等. 珍稀濒危植物金丝李种子的休眠机理[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(5): 1371-1381. |
| ZHANG J J, WEI X, CHAI S F, et al. Dormancy mechanism of the seeds of a rare and endangered plant,Garcinia paucinervis[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(5): 1371-1381. |
| [1] | WEI Xuying, ZHANG Yao, MA Meixia, JIANG Xueru, CHEN Huiting, WU Jing, YANG Yu, CAI Junhuo. Changes of non-structured carbohydrate and starch metabolizing enzyme in bulbs of Lycoris radiata within the annual growth cycle [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2024, 48(1): 106-114. |
| [2] | HU Yongheng, ZHANG Cheng, WAN Huaqin, ZHU Yongli, LI Pingping. Changes of chemical properties during composting of different garden wastes and their effects on germination index [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(6): 133-140. |
| [3] | WANG Xiaojing, WANG Tao, YANG Kai, LI Lubin. Expressional profiling of circRNAs under PEG and NaCl stresses in germinated moso bamboo seeds [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(6): 17-24. |
| [4] | GUO Congcong, SHEN Yongbao, SHI Fenghou. Effects of temperature on stored substance metabolism and enzyme activity during germination of Pinus bungeana seeds [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(6): 25-34. |
| [5] | LIU Rong, WU Dejun, WANG Yinhua, REN Fei, LI Li, YAN Liping, ZHOU Xiaofeng. Screening of optimal germination medium for in vitro Fraxinus [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(3): 70-76. |
| [6] | LIU Xiangquan, ZHAO Renfei, ZHU Yanfang, DENG Shiming, LI Jitao, DENG Zhijun. Mechanisms of seed vigour changes in the canopy seed bank of Koelreuteria bipinnata [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2023, 47(2): 35-41. |
| [7] | WANG Haoyu, GAO Yunpeng, ZHU Mingwei, WU Yang, XU Linqiao, LI Shuxian. Effects of endogenous inhibitors on seed germination of Cercis canadensis [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2022, 46(5): 104-112. |
| [8] | ZOU Yuting, ZHU Mingwei, LI Yongrong, ZHAI Jinting, LI Shuxian. Dynamic changes in nutrients content and related enzymes activity during Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ seeds development [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(5): 62-70. |
| [9] | DENG Ping, ZHAO Ying, WANG Xia, CHEN Qiuyou, WU Min. Effects of salicylic acid on germination of Cyclobalanopsis glauca seeds under NaHCO3 stress in Karst area of northwest Guangxi [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(4): 114-122. |
| [10] | WAN Yawen, FU Huajun, SHI Peijian, LIN Shuyan. Effects of variable temperatures on seed germination and seedling growth of Phyllostachys edulis [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(4): 97-106. |
| [11] | SUN Haiyan, LI Qiang, ZHU Mingwei, LI Yongrong, LI Shuxian. Dynamic changes of nutrients of Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ seed during its dormancy breaking [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2021, 45(1): 70-78. |
| [12] | WANG Ning, YUAN Meili. Seed germination and seedling growth responses of invasive alien plant Aegilops tauschii to saline-alkali stress [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(5): 167-173. |
| [13] | WANG Xiaolei, CUI Xiaokun, ZHANG Peng, SHEN Hailong, YANG Ling. Effects of naked stratification patterns and period on seed germination of Pinus koraiensis Sieb. et Zucc. [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(4): 37-46. |
| [14] | JIANG Nannan, ZHANG Qixiang, WANG Yuan, SUN Yin, FANG Yifu, XU Jinguang. Effects of GA3 on dormancy release, endogenous hormones levels and sugar metabolism in Paeonia lactiflora ‘Da Fugui’ [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(3): 26-32. |
| [15] | WANG Haowei, YANG Ling, LU Qiang, FU Xiangxiang. Effects of salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Cornus florida [J]. JOURNAL OF NANJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY, 2020, 44(3): 89-94. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||