 PDF(1684 KB)
PDF(1684 KB)


Analyses of the temperate forests development and succession stage in Wangqing County based on TWINSPAN
JIA Ke, WANG Xinjie, HE Jingyuan, LU Yan
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 179-186.
 PDF(1684 KB)
PDF(1684 KB)
 PDF(1684 KB)
PDF(1684 KB)
Analyses of the temperate forests development and succession stage in Wangqing County based on TWINSPAN
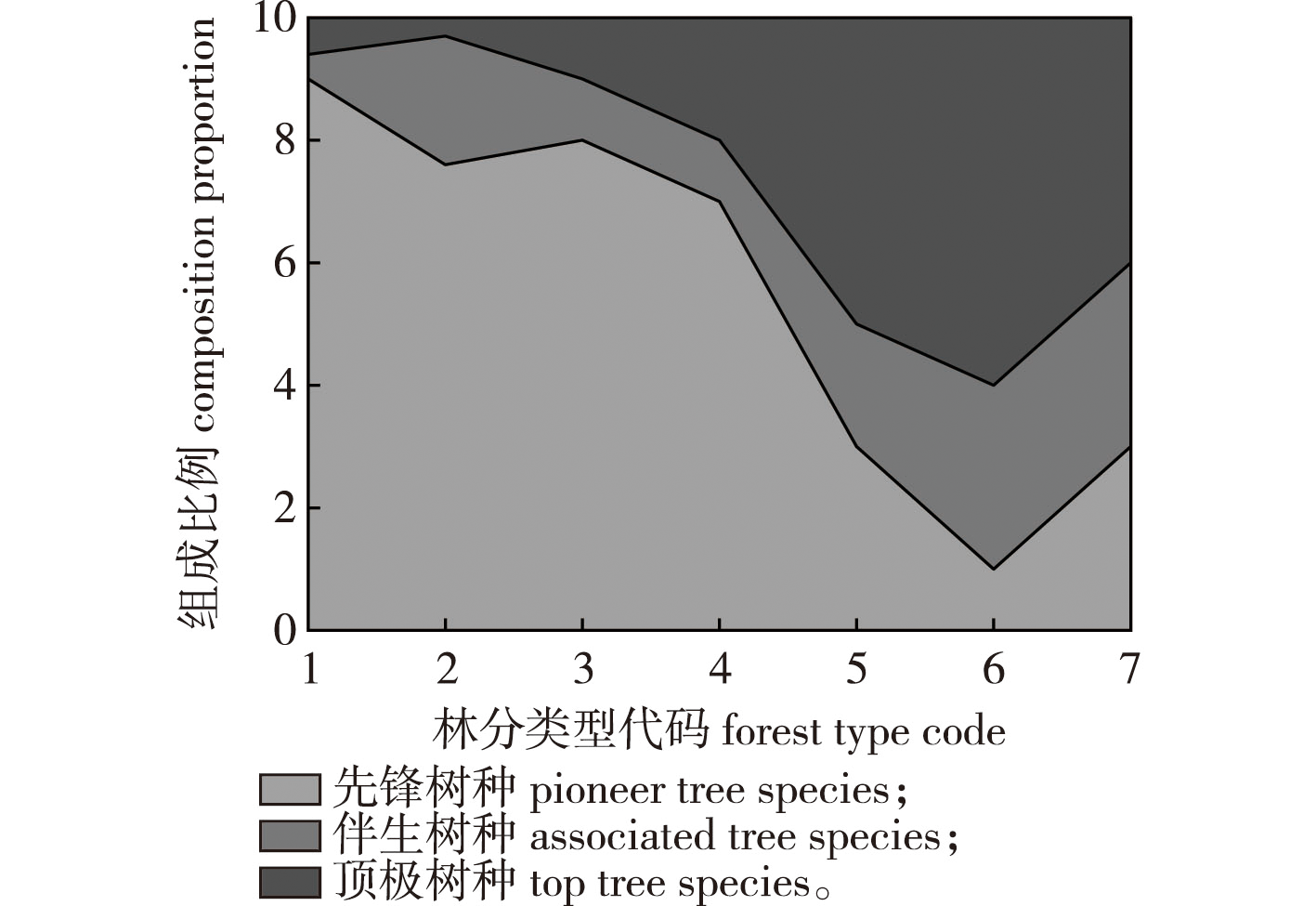
【Objective】 Temperate forests account for nearly 20% of the global forest area. They are scattered and located in densely populated areas that are prone to disturbance and face ecological problems that include loss of species diversity. Accurately classifying the developmental stages of temperate forests, providing methods and theoretical bases for forest management at each stage, and achieving efficient management of temperate forests are urgent problems. 【Method】 In this study, considering the tree species composition of 5 124 subcompartments in the forest resource inventory in Wangqing County, Jilin Province, in 2017 as the research object, the TWINSPAN method was used to reveal the succession stage and development law of temperate forests in this area. Relevant measures of forest management were proposed according to the characteristics of different development stages. 【Results】 Stand structure and growth change indices, such as stand age, average tree height, storage volume per hectare, total storage volume, and number of plants per hectare were selected. The stages of successional development were determined and the temperate forests in the study area were classified into seven categories: mixed broadleaf forest of Betula platyphylla, mixed broadleaf forest of Quercus mongolica, mixed coniferous and broadleaf forest of Q. mongolica, mixed coniferous and broadleaf forest of B. platyphylla and Picea asperata, mixed coniferous and broadleaf forest of P. asperata and B. platyphylla, mixed coniferous and broadleaf forest of Pinus koraiensis and P. asperata, and mixed broadleaf forest of P. koraiensis and Picea asperata. Among these, the mixed coniferous and broadleaf forests of P. koraiensis and P. asperata displayed the largest shared area and constitute the main forest types in the region. The succession characteristics of each forest type were obvious; the top species represented by P. koraiensis and P. asperata, and the companion species represented by Tilia tuan and Acer pictum subsp. mono changed from weak to strong, and the number share gradually expanded. The pioneer species, represented by B. platyphylla and Populus davidiana gradually decreased and finally formed a top community of mixed broadleaf forests of P. koraiensis and P. asperata. 【Conclusion】 Based on a large amount of survey data, this study applied the TWINSPAN classification method to delineate seven successional stages in temperate forests of Wangqing County, summarize the characteristics of each successional stage, and confirm that each successional stage conformed to the characteristics of growth and development in the time gradient. The data provide theoretical support for efficient forest management measures in different successional stages, and provide a reference to maintain the relative stability of forest structure and function to form high-quality and high-yielding forest stands.
temperate forests / TWINSPAN classification / forest succession / developmental succession stage / Wangqing County / Jilin Province
| [1] |
韩素梅. 可持续发展和森林可持续经营[J]. 辽宁林业科技, 2001(3):25-26,31.
|
| [2] |
蒋有绪. 森林可持续经营与林业的可持续发展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2001, 14(2):1-8.
|
| [3] |
沈浩, 姜姜, 周晨, 等. 江西石城不同起源阔叶林碳储量驱动因子分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4): 185-190.
|
| [4] |
张会儒, 汤孟平. 金沟岭林场混交林TWINSPAN分类及演替序列分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 33(1):37-42.
|
| [5] |
中国森林编委会. 中国森林[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社,1997.
China Forest Editorial Board. China forests[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Press, 1997.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
李婷婷, 陆元昌, 张显强, 等. 经营的马尾松森林类型发育演替阶段量化指标研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2014, 36(3):9-17.
|
| [9] |
蔡学林, 张志云, 陈善民. 安远县杉木、马尾松人工林生长规律的研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 1992(6):37-45.
|
| [10] |
李海涛, 贺金生, 倪志诚, 等. 西藏拉孜县草地植物群落的TWINSPAN分类及其物种多样性研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2004, 26(1):31-36.
|
| [11] |
张金屯. 植被数量生态学方法[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社,1995.
|
| [12] |
周梦丽, 雷相东, 国红, 等. 基于TWINSPAN分类的天然云冷杉-阔叶混交林发育阶段划分[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(3):49-55.
|
| [13] |
张新时. 西藏阿里植物群落的间接梯度分析、数量分类与环境解释[J]. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 1991(2):101-113.
|
| [14] |
陈仲新, 张新时. 毛乌素沙化草地景观生态分类与排序的研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 1996, 20(5):423-437.
|
| [15] |
吴菲. 森林立地分类及质量评价研究综述[J]. 林业科技情报, 2010, 42(1):12,14.
|
| [16] |
张文静, 张钦弟, 王晶, 等. 多元回归树与双向指示种分析在群落分类中的应用比较[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(6):586-592.
|
| [17] |
张文丽, 夏会娟, 张远, 等. 东辽河河岸带草本植物物种多样性及群落数量分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(5):1142-1149.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
李伟成, 郑彦超, 盛海燕, 等. 浙江庆元巾子峰国家森林公园植被群落的数量分类与排序[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(3):523-533.
|
| [20] |
苏日古嘎, 张金屯, 张斌, 等. 松山自然保护区森林群落的数量分类和排序[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(10):2621-2629.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
吕飞舟. 基于CSI的蒙古栎林木竞争与分级研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2016.
|
| [23] |
李梦颖. 汪清地区森林生物量遥感估测及空间分布格局研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2017.
|
| [24] |
邢劭朋. 吉林森林[M]. 长春: 吉林科学技术出版社,1988.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
李俊清. 森林生态学[M]. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2017:249-250.
|
| [29] |
唐守正, 刘世荣. 我国天然林保护与可持续经营[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2000, 2(1):42-46.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |